
Oracle Database supports database objects in the relational model and uses object types to convey the concept of the objects. An object type definition consists of an object specification and an object body. The specification declares the attributes, subprograms (functions and procedures) and other object type elements, such as map order functions. The object types are stored in the database itself along with the data. Object types may be used just as any other data types. As an example, a database object type called CATALOG_TYPE may be used in a table definition as follows:
CREATE TABLE catalog (
c1 CATALOG_TYPE,
edition VARCHAR2(25));
Or, an object type may be used to create an object table. An object table is the simplest use of an object type. Each row of data in an object table contains data modelled by the object type from which the object table is created.
Setting the environment
The following steps are required:
- Download and install Toad for Oracle 14 DBA Edition which includes the DB Admin module, as discussed inHow to download Toad for Oracle.
- Create an instance of Oracle Autonomous Database on a local machine or a cloud platform (e.g., Oracle Cloud, Oracle Autonomous Database or AWS RDS). Oracle Database 19c is used in the tutorial.
- Create a connection to the Oracle Database in Toad for Oracle.
How to create a database object
TheCREATE TYPE statement is used to create a database object type. A statement could be directly run in an Editor (SQL Worksheet), but we’ll use the Toad for Oracle built-in tools to model and create an object type. We’ll create an object type called CATALOG_TYPE, which models a journal catalog. The object type consists of attributesid, journal, publisher, a map function called get_id, and a member procedure called get_details. The object specification for the catalog_type object type is as follows:
CREATE TYPE catalog_type AS OBJECT (
id SMALLINT,
journal VARCHAR2 (20),
publisher VARCHAR2 (25),
MAP MEMBER FUNCTION get_id RETURN SMALLINT,
MEMBER PROCEDURE get_details (SELF IN OUT NOCOPY CATALOG_TYPE));
The object body for the catalog_type object type is as follows:
CREATE TYPE BODY catalog_type AS
MAP MEMBER FUNCTION get_id RETURN NUMBER IS
BEGIN
RETURN id;
END;
MEMBER PROCEDURE get_details (SELF IN OUT NOCOPY CATALOG_TYPE) IS
BEGIN
— use the PUT_LINE procedure of the DBMS_OUTPUT package to display details
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(TO_CHAR(id) || ' ' || journal || ' ' || publisher);
END;
END;
When developing a new object type, the complete definition may not be known at the outset and may be modelled as discussed next. Select Database>Create>Schema>Object from the toolbar (Figure 1.).
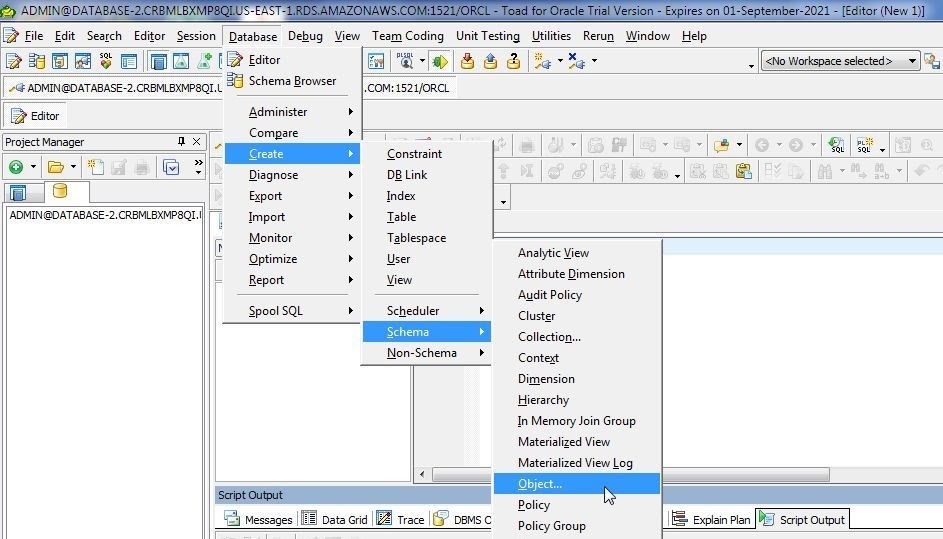
Figure 1. Database>Create>Schema>Object
The Create Object Type dialog is displayed (Figure 2.).
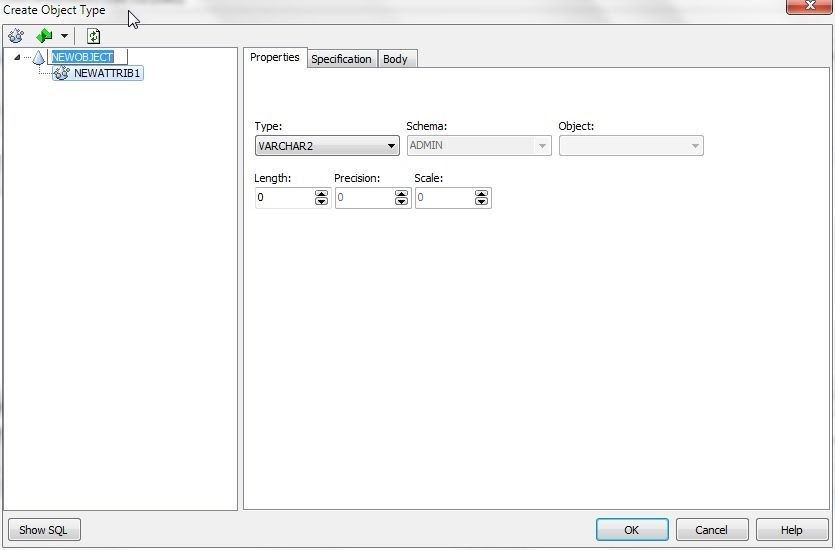
Figure 2. Create Database Type
First, rename the placeholder object type. Right-click on the NEWOBJECT dummy object type and select Rename (Figure 3).
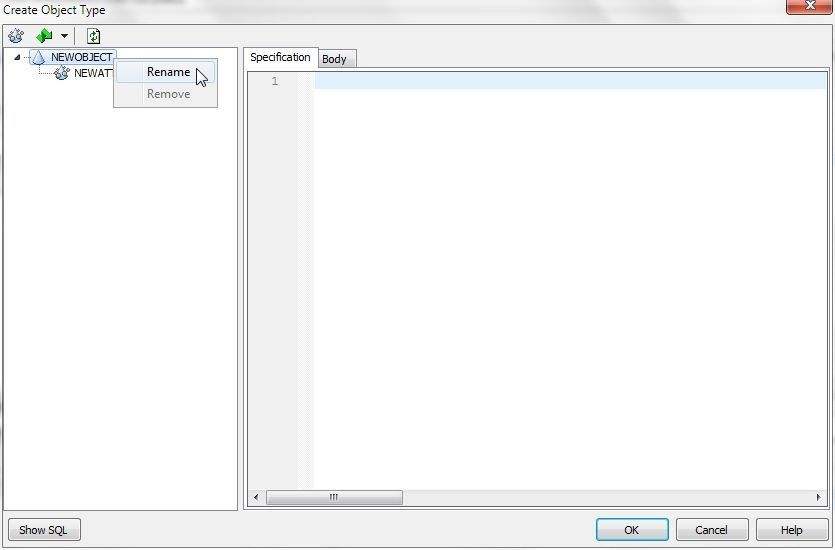
Figure 3. Renaming dummy object type
Similarly, rename the first placeholder attribute with right-click>Rename to id (Figure 4).
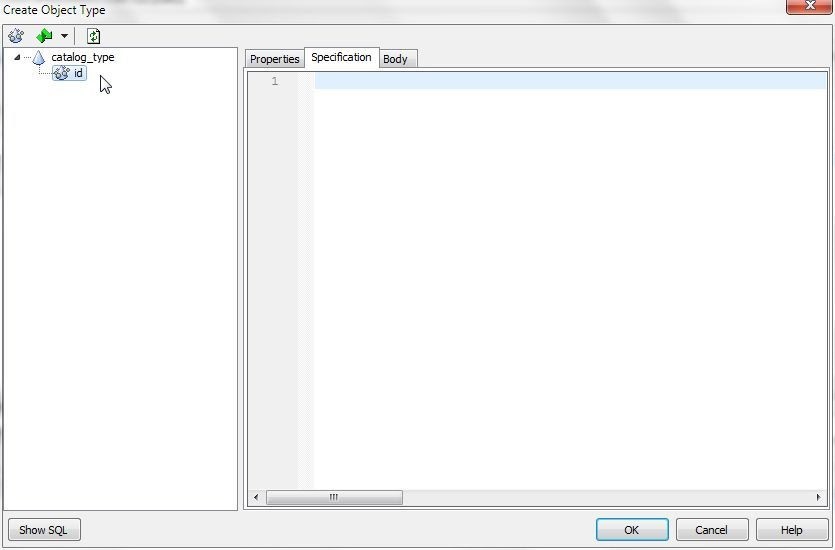
Figure 4. Renamed attribute in object type CATALOG_TYPE
Additional attributes may be added by selecting New Attribute (Figure 5).
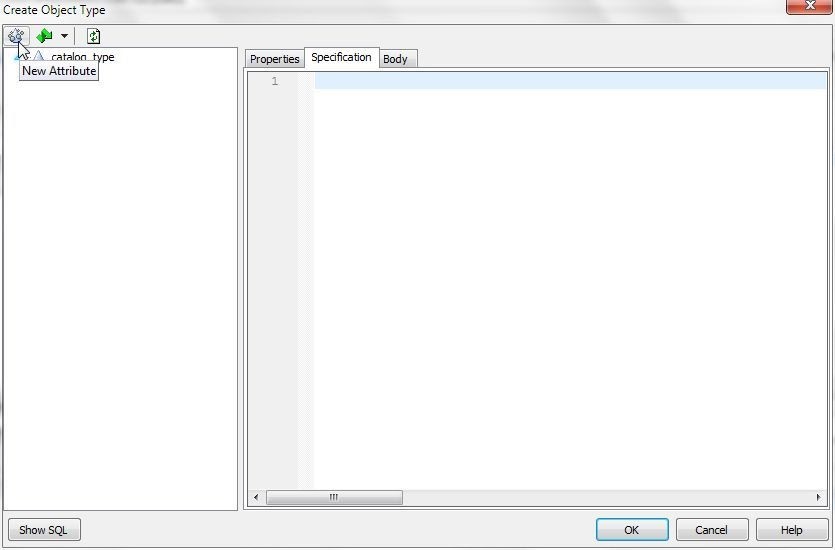
Figure 5. New Attribute
Rename the placeholder attribute added by selecting Rename on a right-click, as before. An attribute’s properties may be set in the Properties tab. Set the publisher and journal attributes to Type VARCHAR2 (Figure 6).
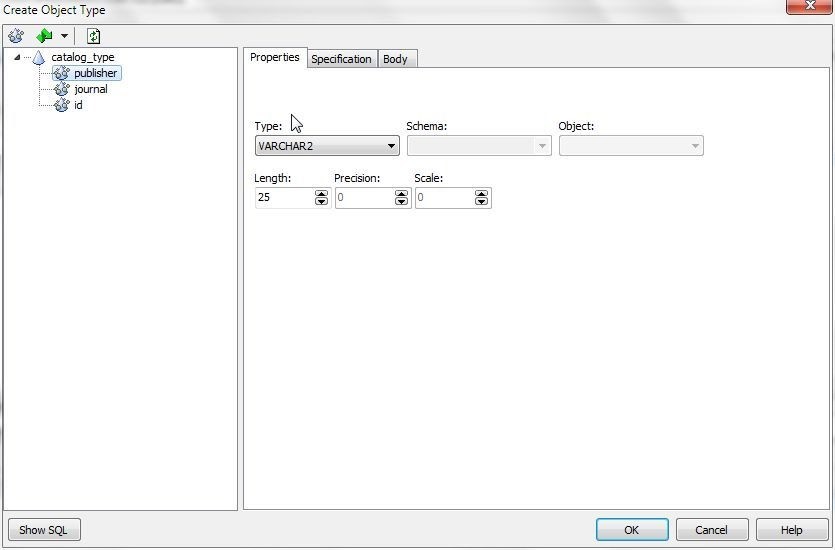
Figure 6. Setting publisher attribute type to VARCHAR2
Set the id attribute to type SMALLINT (Figure 7).
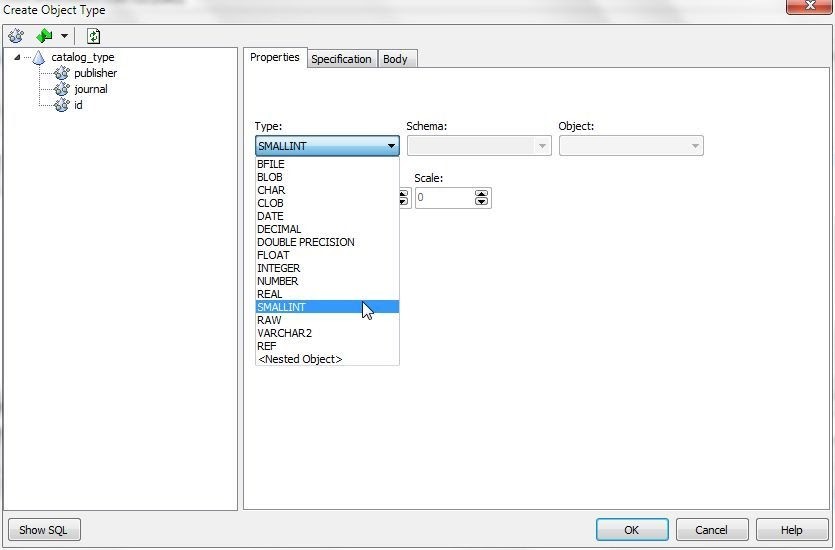
Figure 7. Setting idattribute to SMALLINT type
To add a map function, select New Map Function (Figure 8) from the drop-down in the toolbar.
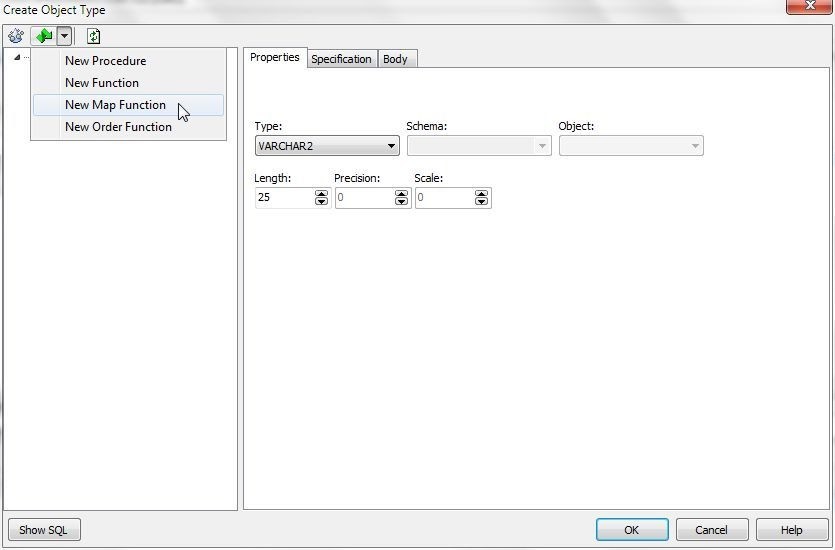
Figure 8. Adding New Map Function
A placeholder map function gets added. Rename the map function to get_id, and set return type to SMALLINT (Figure 9).
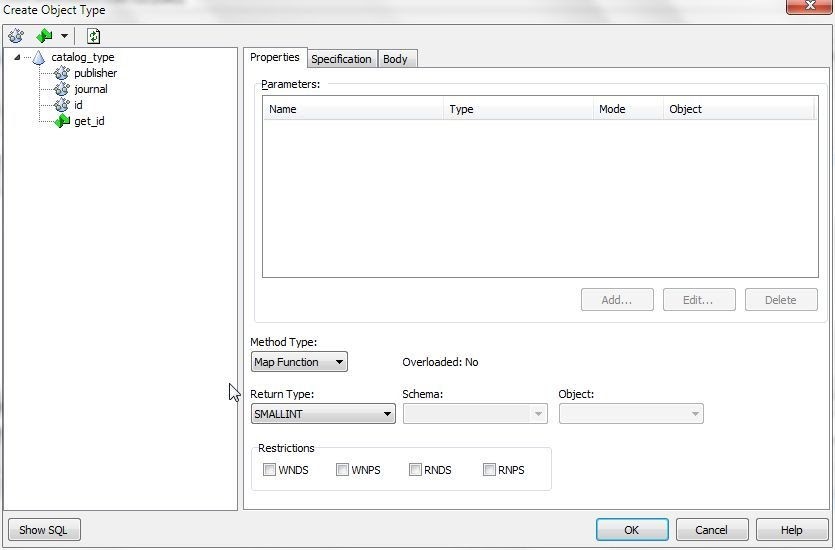
Figure 9. Map Function get_id
To add a member procedure, select New Procedure (Figure 10) from the toolbar.
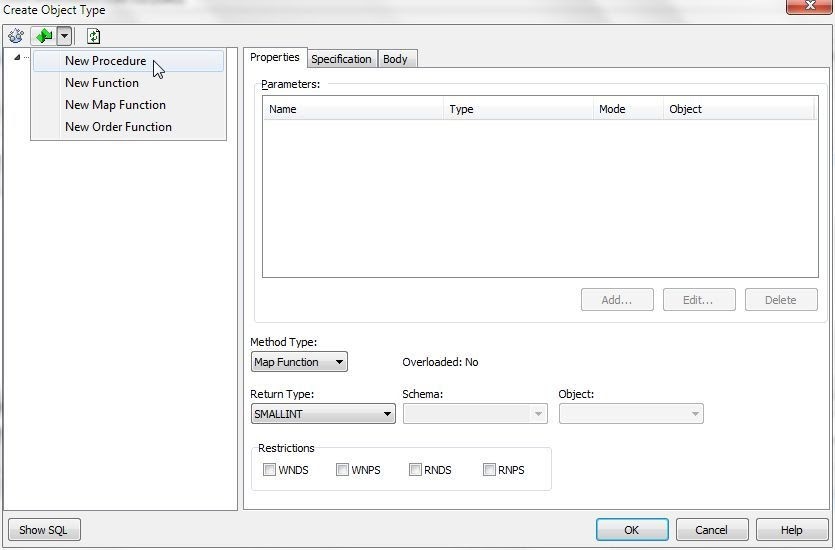
Figure 10. New Procedure
A placeholder procedure gets added to start with. Rename procedure to get_details with right-click>Rename. Procedure parameters may be added with the Add button (Figure 11) .
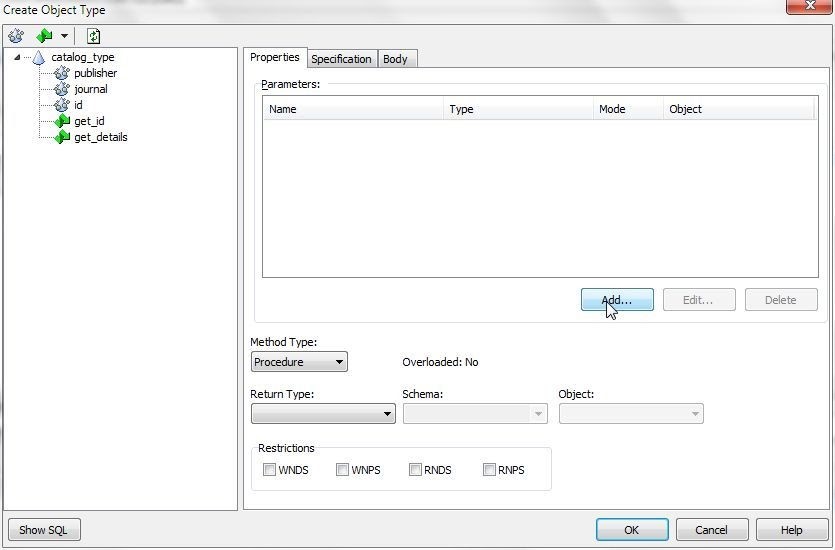
Figure 11. Procedure
Click on Show SQL (Figure 12) to generate and show the SQL for the new object type.
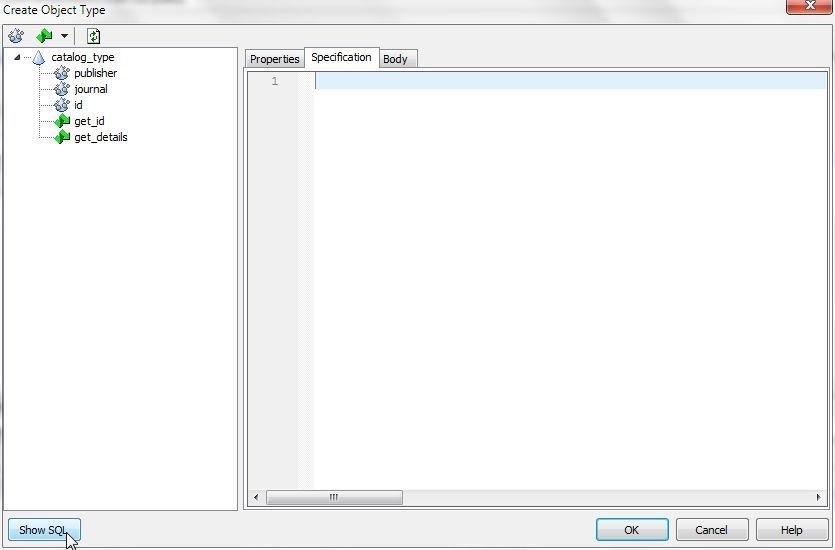
Figure 12. Show SQL
The SQL for the database object type specification is displayed in the Specification tab. The Body tab displays the object type body. The complete SQL statement for the object type definition is displayed in a pop-up window when Show SQL is clicked. With a start script for the new object type, send the SQL statement to an Editor with Send to Editor (Figure 13). Click on OK in the Create Object Type window to close the wizard if no other object type attributes, functions or procedures need to be added.
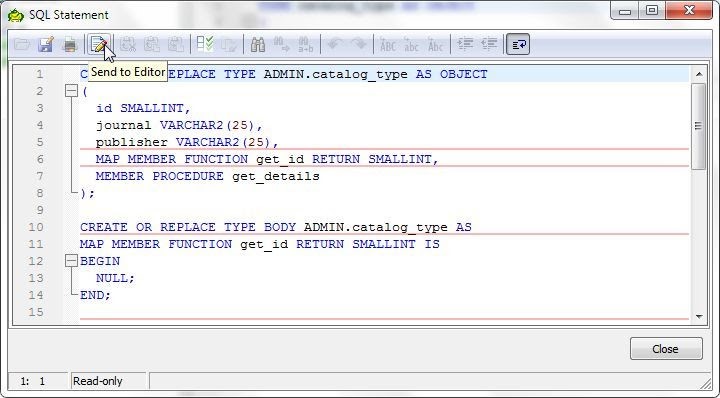
Figure 13. Send to Editor
Modify the SQL script sent to the Editor to make it as listed at the start of this section. Click on Execute Script (Figure 14) to run the script.
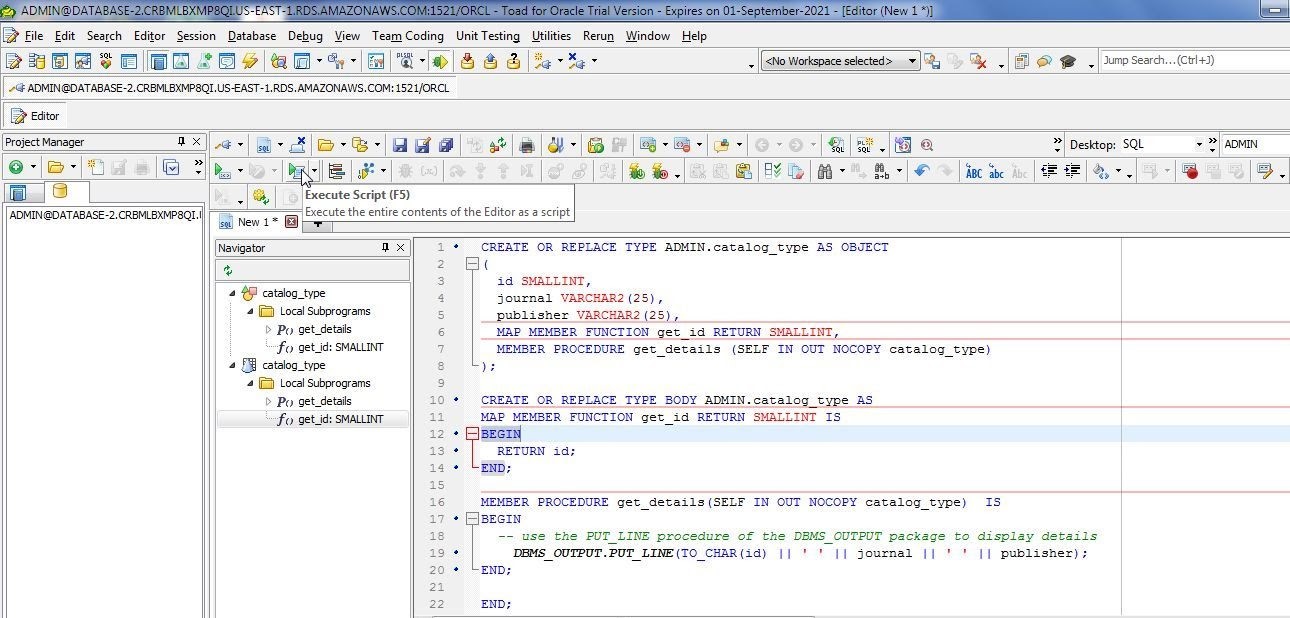
Figure 14. Execute Script
As the Output tab (Figure 15) indicates, the object type is created.
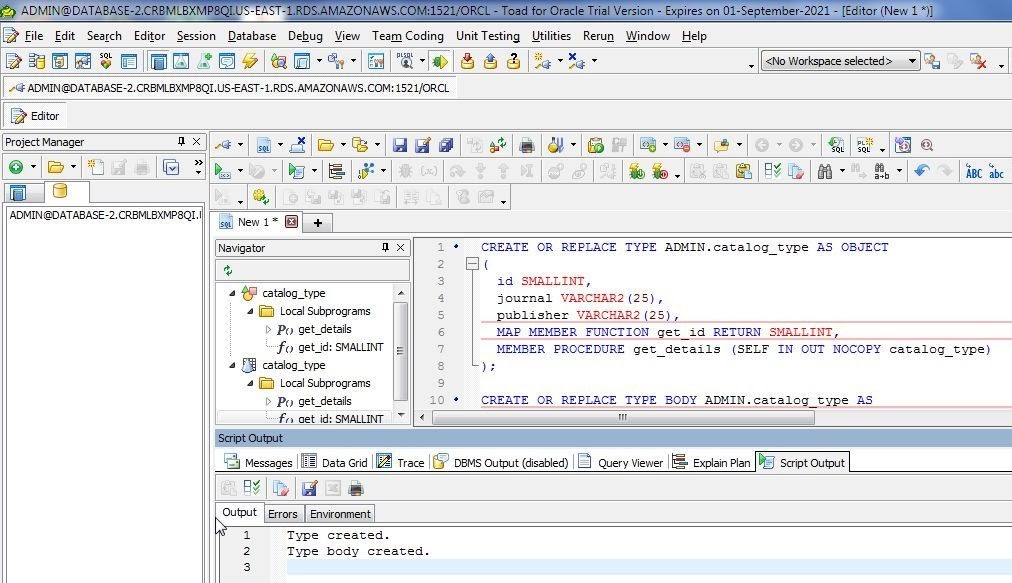
Figure 15. Object type is created
The new object type is stored in the database itself. To verify, select Database>Schema Browser from the toolbar (Figure 16).
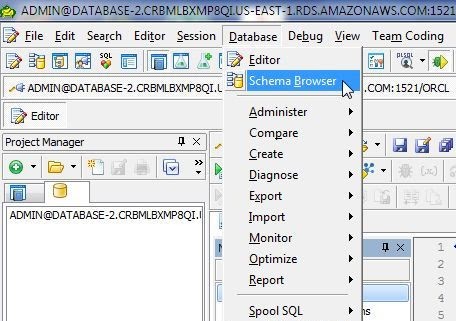
Figure 16. Database>Schema Browser
SelectTypes from the drop-down in the Schema Browser. The new object type called CATALOG_TYPE that we created is listed (Figure 17).
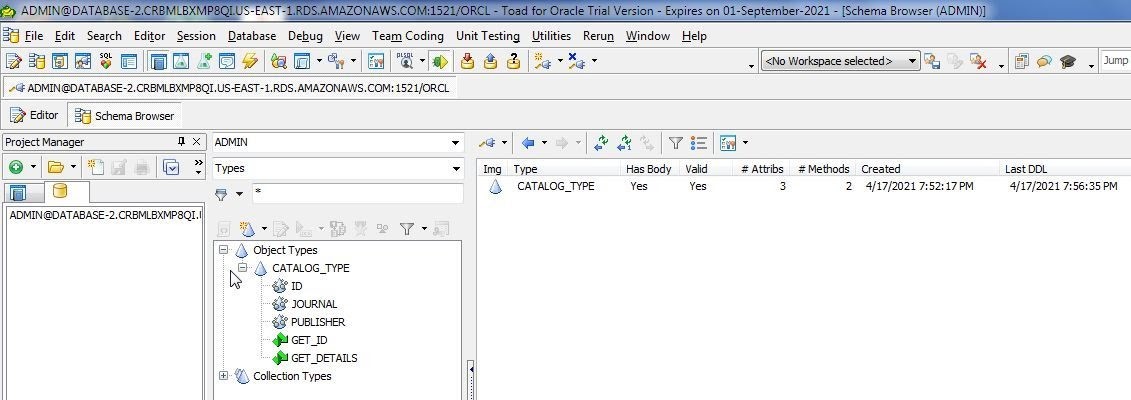
Figure 17. Object Type CATALOG_TYPE
Click on the CATALOG_TYPE object type to list its details in various tabs. The Info tab (Figure 24) lists the basic information about the object type. The Attributes & Methods tab (Figure 18) lists the attributes and methods.
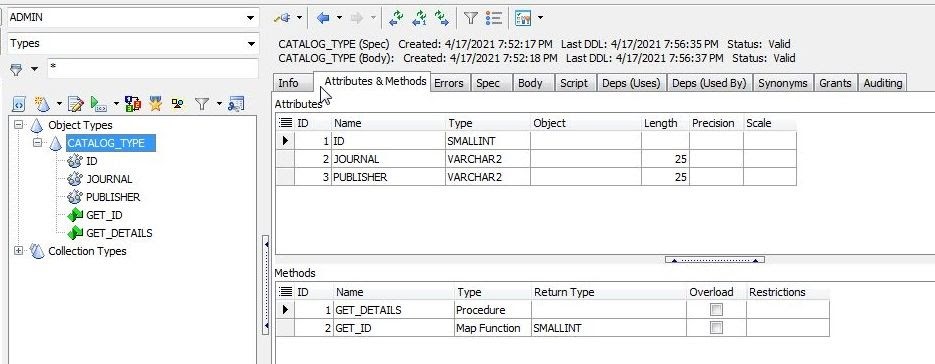
Figure 18. Attributes & Methods
The Spec tab lists the object specification (Figure 19).
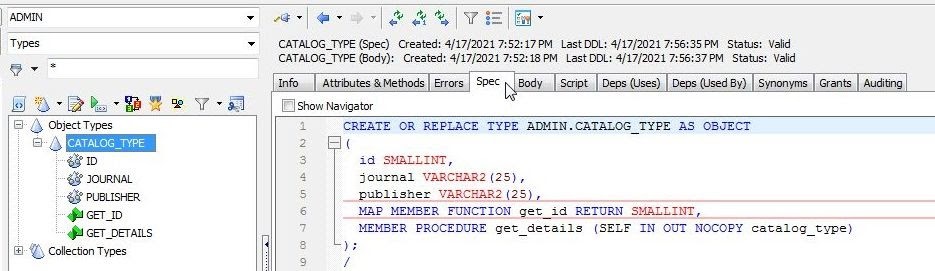
Figure 19. Spec tab
And the Body tab lists the object body (Figure 20).
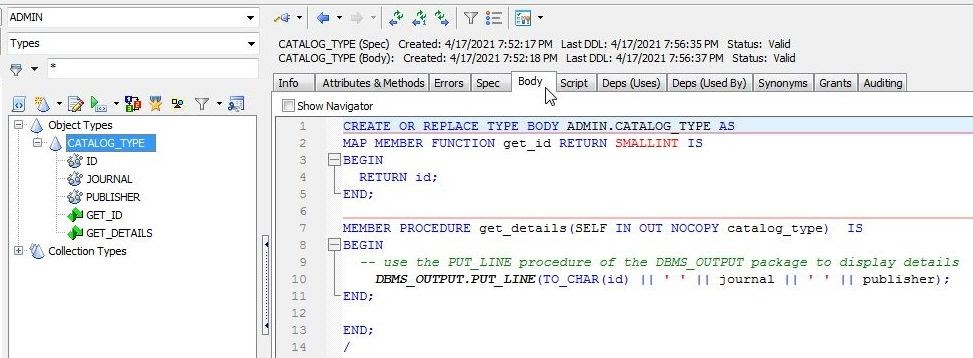
Figure 20. Body tab
Get Toad for Oracle Base Subscription todaySubscription / eStore: buy up to 10 licenses at a time, get auto update, support, announcements/invites to education. Talk to our professionals: demos, custom solutions, volume discounts. Not ready to buy? Get Toad for Oracle a 4th way … try it free for 30 days. |
How to create an object table
Next, create an object table from the new object type CATALOG_TYPE. A new object table may be created with an SQL statement such as the following:
CREATE TABLE catalog_obj_table OF CATALOG_TYPE;
But, we’ll create an object table using the built-in tool. Right-click on CATALOG_TYPE in the Schema Browser, and select Create>Object Table (Figure 21).
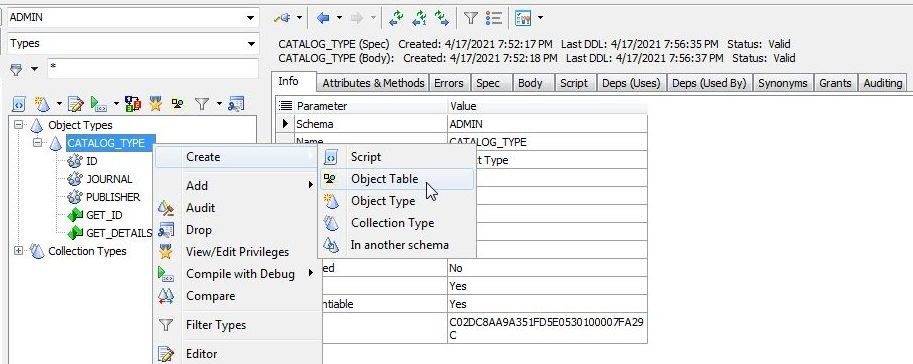
Figure 21. CATALOG_TYPE>Create>Object Table
Alternatively, select Create Object Table (Figure 22).
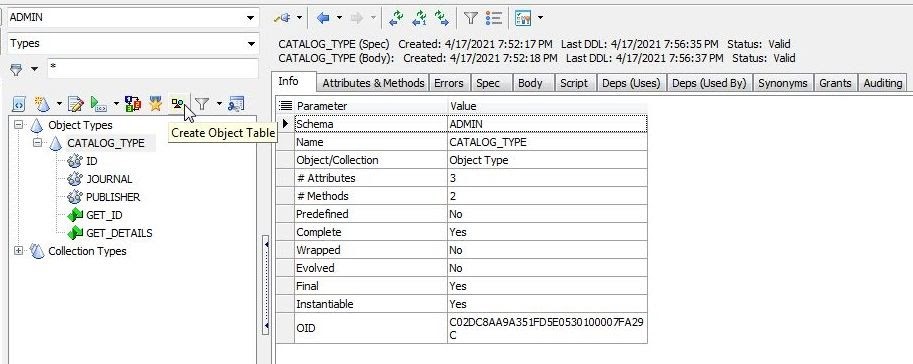
Figure 22. Create Object Table
An Information dialog gets displayed to indicate that the script was run without any errors. Refresh the Schema Browser, such as by closing and reopening it. Select Tables from the drop-down. The object table CATALOG_TYPE_T gets listed (Figure 23).
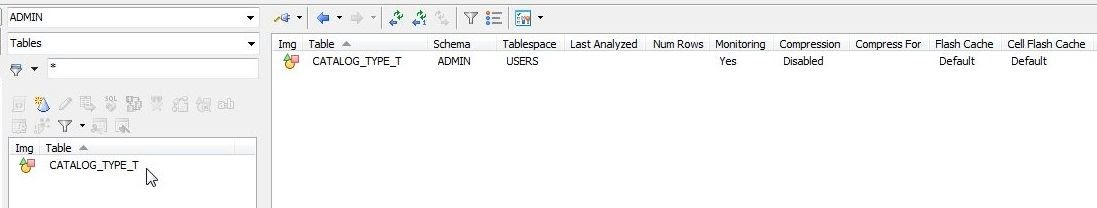
Figure 23. New Object Table
The new object table does not have any data in it as shown by the Data tab (Figure 24).
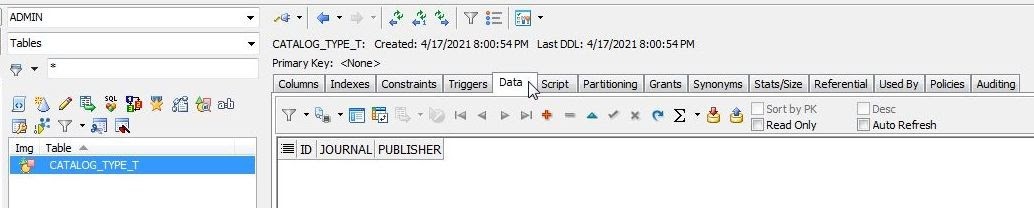
Figure 24. Data tab
To add data to the object table, copy the following PL/SQL script to a new SQL worksheet (Editor).
DECLARE
BEGIN
INSERT INTO CATALOG_TYPE_T VALUES (CATALOG_TYPE(1, 'Oracle Magazine', 'Oracle Publishing'));
INSERT INTO CATALOG_TYPE_T VALUES (CATALOG_TYPE(2, 'Java Magazine', 'Oracle Publishing'));
END;
Click on Execute Script to run the script. The Output tab indicates that the PL/SQL procedure successfully completed (Figure 25).
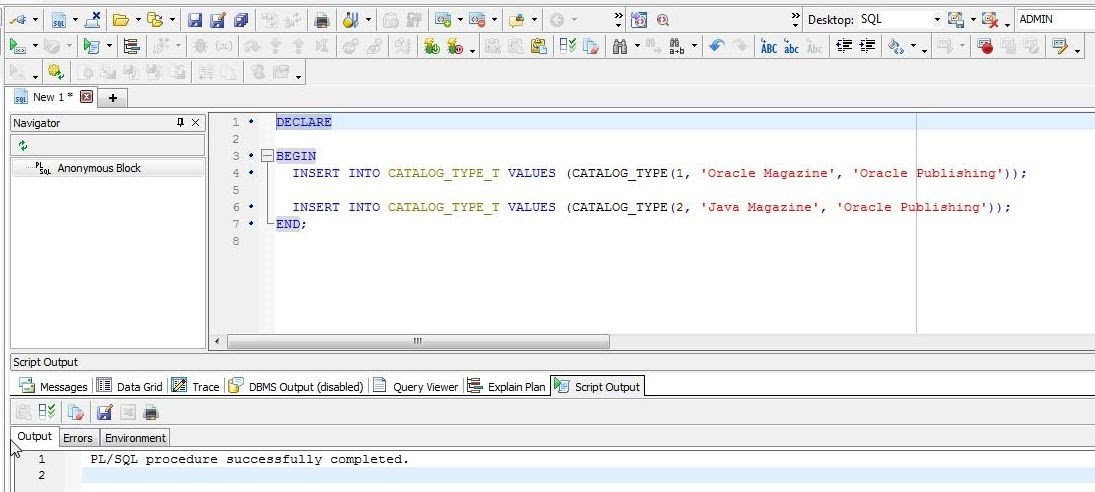
Figure 25. PL/SQL procedure successfully completed
To query the object table copy the following PL/SQL script to a SQL worksheet (Editor).
DECLARE
catalog CATALOG_TYPE;
BEGIN
SELECT VALUE(c) INTO catalog FROM CATALOG_TYPE_T c WHERE c.id = 1;
catalog.get_details();
END;
Click on Execute Script to run the script. The Output tab indicates that the PL/SQL procedure completed successfully. The DBMS Output tab (Figure 26) displays the query result.
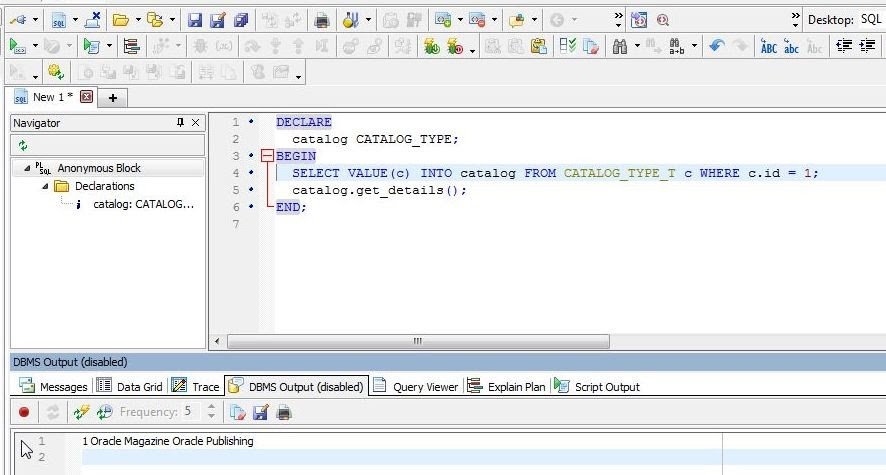
Figure 26. DBMS Output tab
In a continuation article we’ll discuss altering an object, and dropping an object.
What’s Next?
- Explore and Select a Toad product at https://support.quest.com/download-product-select
- Download Free Trial Version of Toad for Oracle from https://www.quest.com/register/54618/
- Buy Online or Request Pricing for Toad for Oracle at https://www.quest.com/products/toad-for-oracle/
- Get Product Support for Toad for Oracle at https://support.quest.com/
Have questions about Toad Developer Tools? Click Start Discussion and this blog topic will be transferred to the Toad World Forums.
Related information:
Blog: DB performance: 6 benefits from maintaining database health and stability
Data sheet: Toad for Oracle DB Admin Module.
Blog: Toad SQL Editor Code Templates
Blog: Toad Explain Plan More Advanced Options
Blog: Quick and Easy SQL Optimization with Toad for Oracle
Video: VIDEO TUTORIAL: Toad Advanced Explain Plan Tips and Techniques
Video: Video: 'Dan's Dozen' Quick Toad Tips – Tip #5 – Advanced Explain Plans
Blog and Video Demo: Why an Oracle Ace thinks Toad® has the best SQL editor in the business
Oracle Documentation: Explain Plan Content
Oracle Documentation: Explaining a SQL statement: Basic Steps
Webcast: Five Cool DBA Features in Toad for Oracle Base Edition
Webcast: Top Five Use Cases for Developers for Toad for Oracle Base Edition
Chapter 10 “Toad as a SQL Tuning Tool” in Toad for Oracle Unleashed.
Blog: DB performance: 120-point database health check across multiple databases
Help your colleagues
If you think your colleagues would benefit from this blog, share it now on social media with the buttons located at the top of this blog post. Thanks!


Start the discussion at forums.toadworld.com