Part 3. With the rise of cyber security threats, application security is certainly getting more attention. CIOs, CISOs and other executives, responsible for implementing data protection strategies in their company, need to make sure they are protecting their corporate data, comply with the appropriate data privacy regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI and others and prevent breaches, fines and reputational damage that could seriously impact their business.

Some industry sectors, such as financial services, are increasingly being mandated to apply security patches to operating systems and desktop software to minimize any vulnerabilities.
In Part 1 of this three-part blog series, I introduced the need for tighter application security and why it’s incumbent on software vendors like Quest® to ensure their applications are as secure as they can be.
In Part 2 of this 3-part blog series, I outlined some further security controls that Quest performs on Toad to ensure it’s as secure as it can be.
In this final part, I’ll walk you through the final group of security controls that Toad is subject to ensure it adheres to current software security standards for continually testing and delivering new versions that you can safely install and run.
You’ll also see a compelling argument for staying up to date with the frequent releases of Toad products so you can avoid vulnerabilities and security threats in the future.
Update your Toad for free, with a current licenseIf you want an update/install from Quest for any Quest product, you need three things:
Your login will be tied to your Toad license. If it’s current, it will let you login to ask questions and get downloads. If you’re denied these because of maintenance issues, you’ll be contacted very soon by a Quest rep who can make sure your account information is correct or offer to update your maintenance agreement. |
Security controls for preventing supply chain attacks
Most IT administrators are occupied with plugging security gaps among different applications installed on different platforms. That’s why Quest believes in making security practical by releasing products that are secure in the first place.
The table below shows the security controls which every release of Toad undergoes.
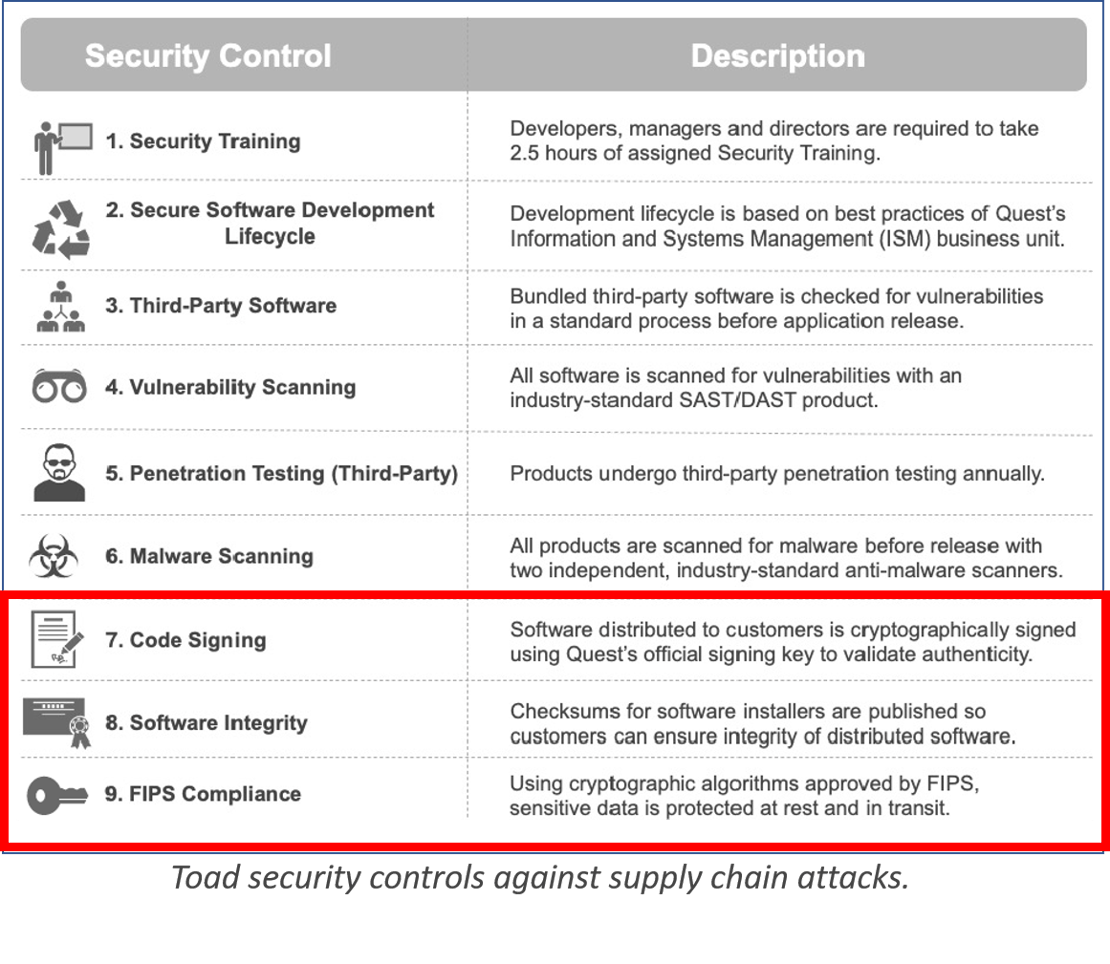
In this blog, we’re going to look at the final 3 controls (outlined in red above) and how Quest Software implements each of these controls for Toad products.
Security controls #7, #8: Code signing and software integrity
An application bearing Quest’s code signing certificate is a customer’s assurance that Quest created the application and that the software can be trusted. The code signing process serves the goal of ensuring authenticity by verifying the author of the software. It also ensures the integrity of the software by demonstrating that the code has not been altered since it was signed.
Code signing also plays a role in releasing updates and patches. When Quest signs an update to a Toad product with the same key used in the original application, it means that the update can be trusted; it couldn’t have come from any source other than Quest. Finally, the checksums generated in code signing assure users that they have received the correct file, rather than a file that has been signed with a stolen key.
All major operating systems and web browsers support code signing to prevent the distribution of malicious code.
Quest signs all releases of Toad products using a trusted Quest key. During the build process, Quest signs every .exe and .dll file included in the installer, along with any binaries packaged with the application and the installer files themselves. Applications available for download include a SHA-256 checksum hash so that customers can verify the integrity of the file upon receipt.
Security control #9: Protecting sensitive data through FIPS compliance
The presence of sensitive data in your applications and databases imposes a burden of protection. Sensitive data extends to almost any kind of data you would want to prevent from falling into the wrong hands, including things like credit card information, Social Security numbers, personal health information and financial information.
Toad products protect sensitive data through cryptographic algorithms that conform to the Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) of the United States government. Furthermore, they apply that protection to sensitive data both in transit and at rest.
The FIPS standards specify the best practices and requirements for cryptography-based security systems, including specific methods for encryption and for generating encryption keys. FIPS compliance is mandatory for all computers used for U.S. government work and extends to testing outside applications (like Toad) that will run on U.S. government computers.
All Quest products comply with FIPS-approved algorithms for encryption and hashing. The current status of FIPS compliance (currently FIPS 140-2) is validated prior to each release.

Conclusion
All of the security controls described above, and in the previous two blogs, are designed and applied to mitigate the risk of supply chain security in Toad.
Toad products are valued and trusted, and they have unlocked millions of hours of productivity gains for database professionals.
Make sure you upgrade your Toad to ensure a continual flow of new features and adherence to the latest software security standards. You also receive full technical support and keep your organization’s security profile tight.
Next Steps
For more detailed information on how Toad addresses desktop security through SSDLC, read this Technical Brief.
Watch the free webinar, "Why do you need to update your Toad for Oracle today?"
Try Toad for Oracle nowTry Toad for Oracle free for 30 days. Already in a trial? Talk to sales or buy now online. Already a loyal fan of Toad for Oracle? Renew now. |

Start the discussion at forums.toadworld.com