Hybrid Cloud management is an interestingly hot topic for today’s cloud world, since not all companies want to move everything to the cloud. In this article series, we are looking at the detailed steps for setting up the Oracle Hybrid Cloud via the latest version – Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control 13c installed on premises. Our main intention is to install an Enterprise Manager hybrid cloud agent on our database cloud servers (on the Oracle public cloud) via the hybrid gateway, in the scenario where our company has databases running on premises as well as on the Oracle public cloud, and then to look at hybrid cloud management using Enterprise Manager.
In the previous parts of the article series, we completed the pre-setup steps for the hybrid cloud – such as setting up one of our on-premises Enterprise Manager Oracle Management Service (OMS) agents as the hybrid gateway agent, creating SSH keys for the OMS server, and creating a named credential with SSH key credentials for the hybrid cloud. At the same time, we also created an Oracle Database service (a server with an Oracle database) on the Oracle public cloud.
Next, we completed the installation of the hybrid cloud agent via Oracle Enterprise Manager, which performed a background transfer of the agent software to the destination host. We logged into the on-premises Enterprise Manager console as SYSMAN or a super administrator and drilled down to the Cloud Host home page. On this page, we could see the Enterprise Manager Configuration and performance metrics for the host; these metrics had been uploaded by the hybrid cloud agent. And after the database discovery process was completed, the cloud database appeared in the list of Enterprise Manager database targets, and it can now be monitored and managed just like a normal on-premises database.
Next, we compared Oracle database configurations by selecting Enterprise | Configuration | Comparison and Drift Management from the Enterprise Manager console, and creating a comparison. We selected the on-premises 12c database “ahuprod.sainath.com” and the Cloud database AHUTEST. Effectively, we compared the configuration of a local on-premises database with that of a cloud database. This comparison can be done at the server level as well, and configurations at a certain date and time can be saved as a “Gold” configuration to compare to current configurations at regular intervals, to detect configuration drift. Oracle Enterprise Manager is also able to enforce the same compliance standards on the Oracle public cloud as well as on premises, which is perfect for a hybrid database setup.
Then, we looked into the cloning of PDBs from on premises to cloud, one of the main features of the hybrid cloud. To proceed with the actual PDB cloning, we made sure the source and destination CDBs were at the latest PSU. We then went through the steps to preserve the Enterprise Manager agent home when patching the cloud database. Next, we started the Clone to Oracle cloud process. This was done via right-clicking on the on-premises PDB “SALES”, which is in the ahuprod CDB, and selecting Oracle Database | Cloning | Clone to Oracle Cloud.
The name of the destination PDB on the cloud side was entered as “SALESTST”, since this will be a test pluggable database. We also selected a user name and password for the PDB administrator of the new PDB. Then, we could have clicked on “Clone” to start the procedure, but instead we clicked on the “Advanced” button at the top of the page. This switched to advanced mode, and a multiple page workflow appeared on the same screen.
We clicked on Next. The “Clone to Oracle Cloud: Configuration” page appeared. As per cloud database standards, based on Oracle Flexible Architecture (OFA) standards, the PDB data files will reside on /u02, in the /u02/app/oracle/oradata/<PDB name> directory. You can also enter storage limits if you wish, such as the maximum PDB size or the maximum shared TEMP tablespace size. The default logging attribute for tablespaces creating with the PDB can also be specified – Logging, No Logging or Filesystem Like Logging.
After this, the Post Processing page appeared. This page showed us the importance of the Advanced mode, since it is possible to select a Data Masking Definition if it has been created for the source database. Masking is seamlessly integrated with Enterprise Manager. This makes sure that confidential data is masked when being cloned from an on-premises production database to a cloud development database.
A simple masking definition had already been created. This definition was named “LatestDataMaskDefinitionHR” (no spaces should be included in the definition name) and was selected at this point. This will mask some of the confidential columns in the Employees table, in the destination Cloud PDB that will be created.
In the Schedule screen that appeared next, you scheduled the job and could also choose to be notified on a certain status such as Action Required, Suspended or Problems.
Click Next. Finally, the Review screen appears (Figure 31).
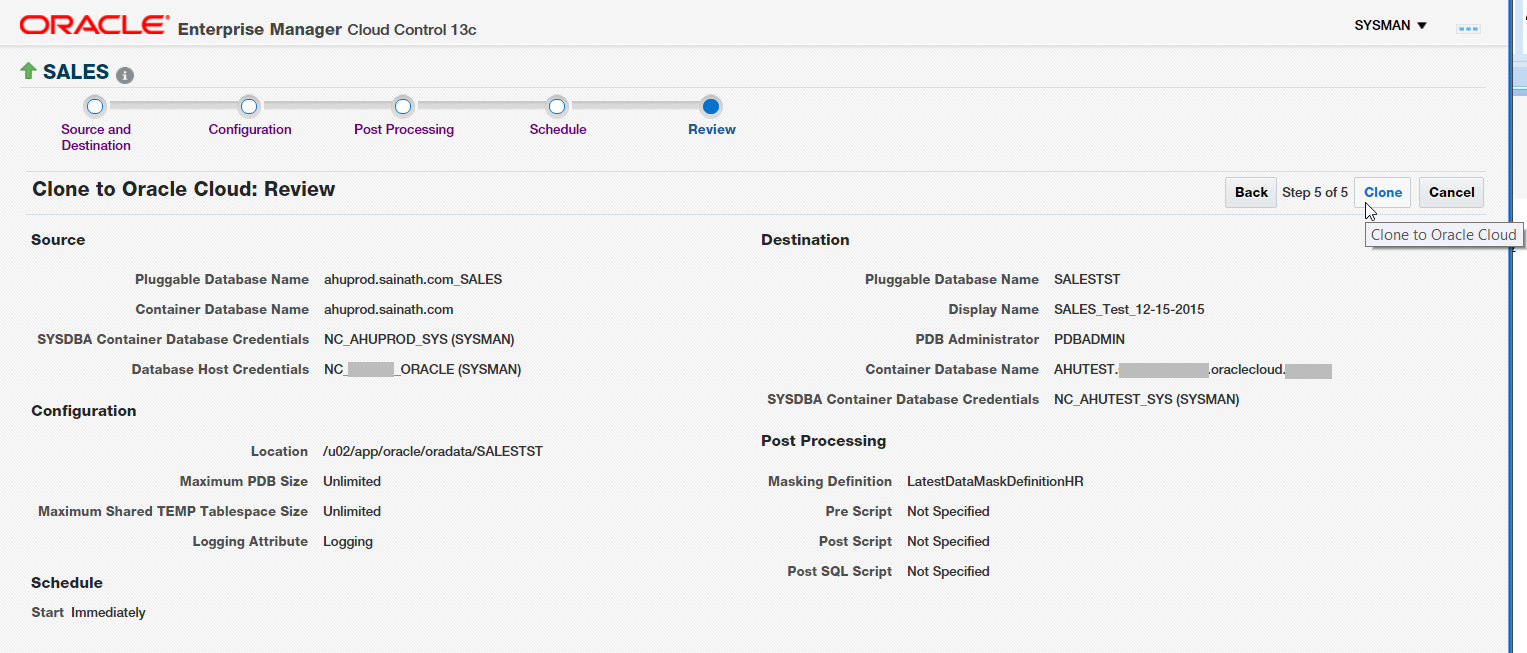
Figure 31: Clone to Oracle Cloud: Review
Review the information, and click on Clone. The procedure starts to execute (Figure 32).
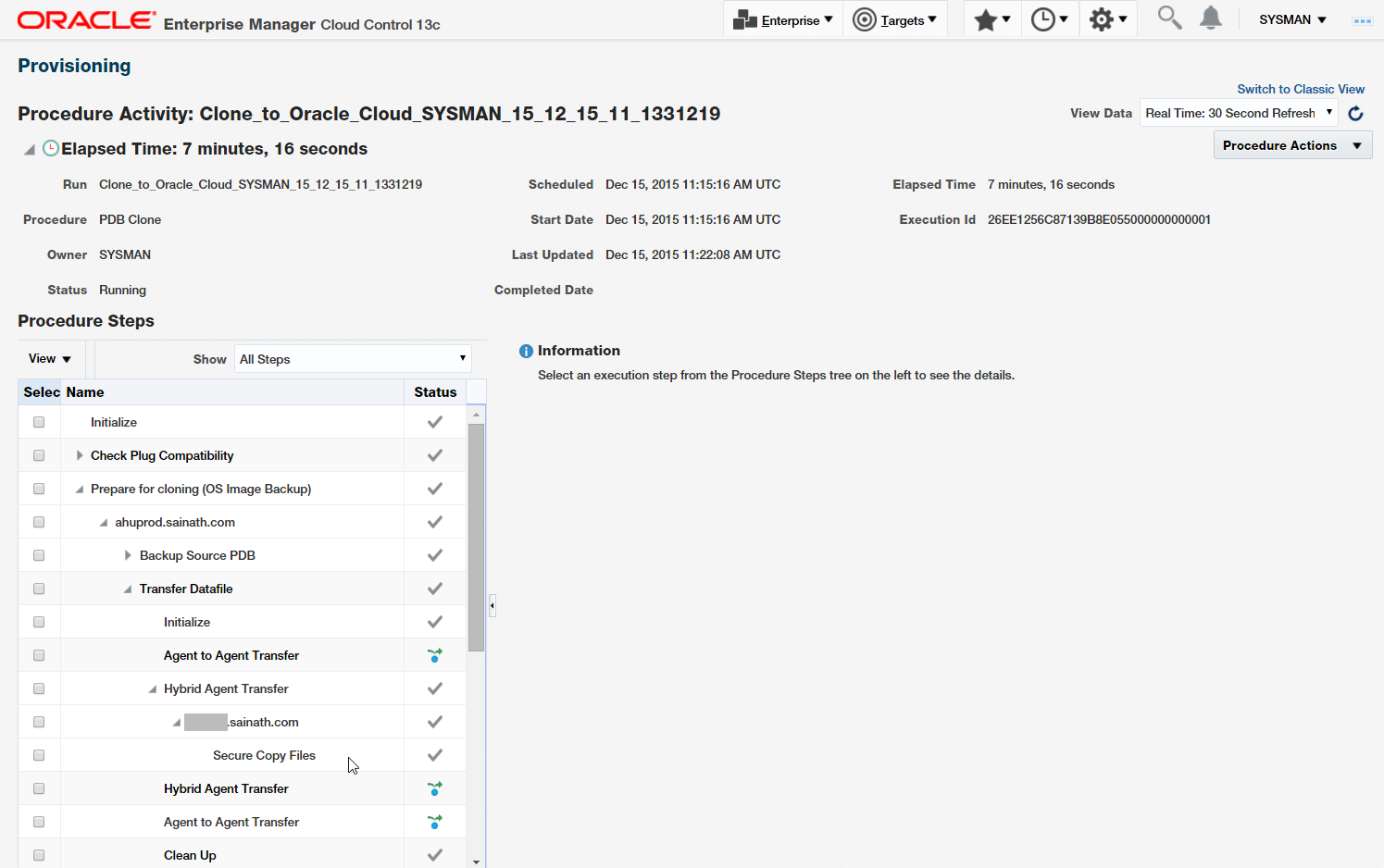
Figure 32: Cloning to Cloud Execution
In the list of Procedure steps, we can see a Secure Copy files step. Note that the “rsync” UNIX command is being used by the procedure to fast-copy files to the cloud.
The clone to cloud completes successfully in under 16 minutes (depending on the PDB size and the Internet connectivity), as can be seen in Figure 33. You can examine each step and its output if you wish.
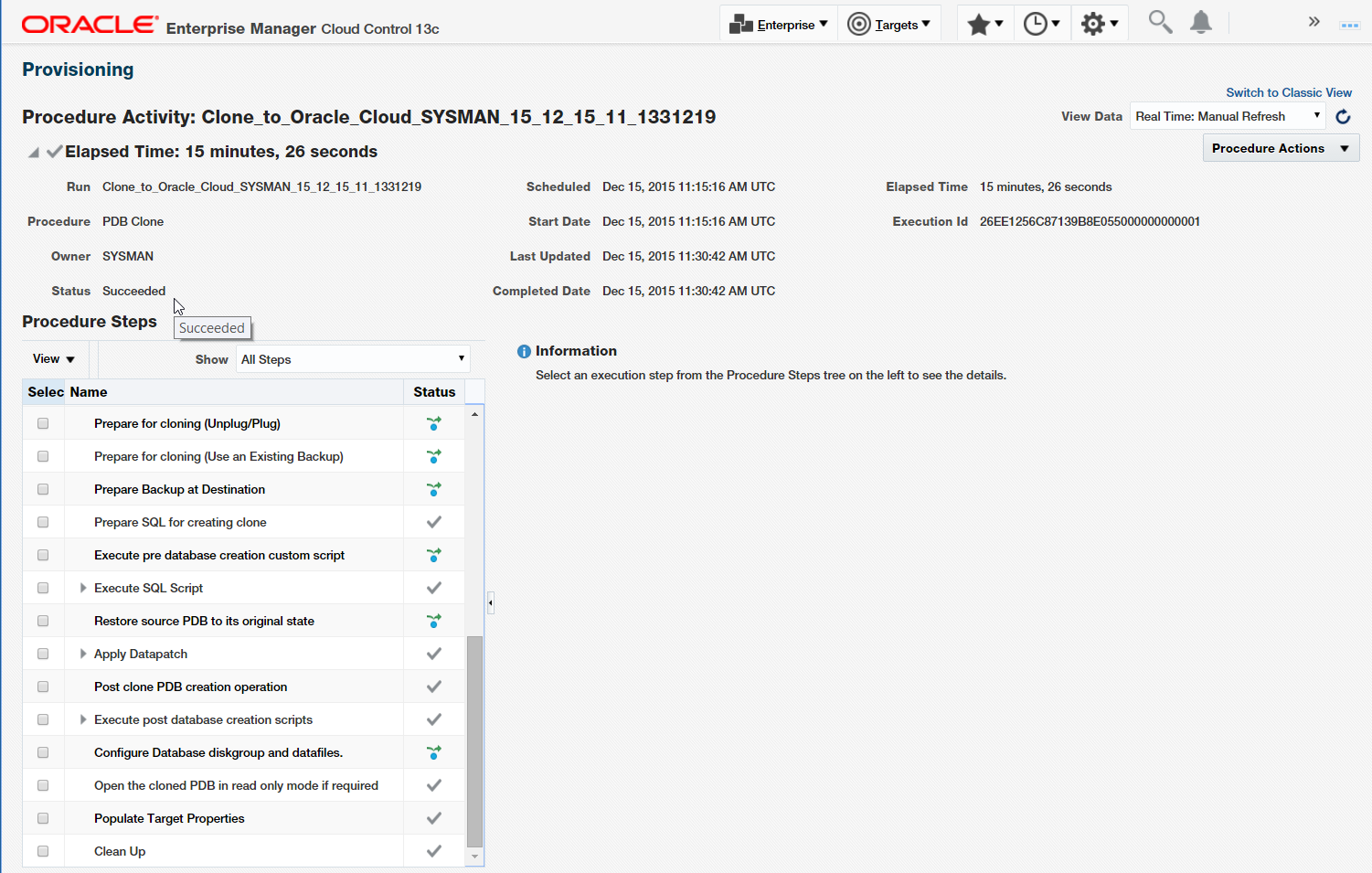
Figure 33: Completed Clone to Cloud
When you move to Targets | Databases, you can now see the new SALES Test PDB under the cloud CDB AHUTEST. This is seen in Figure 34.
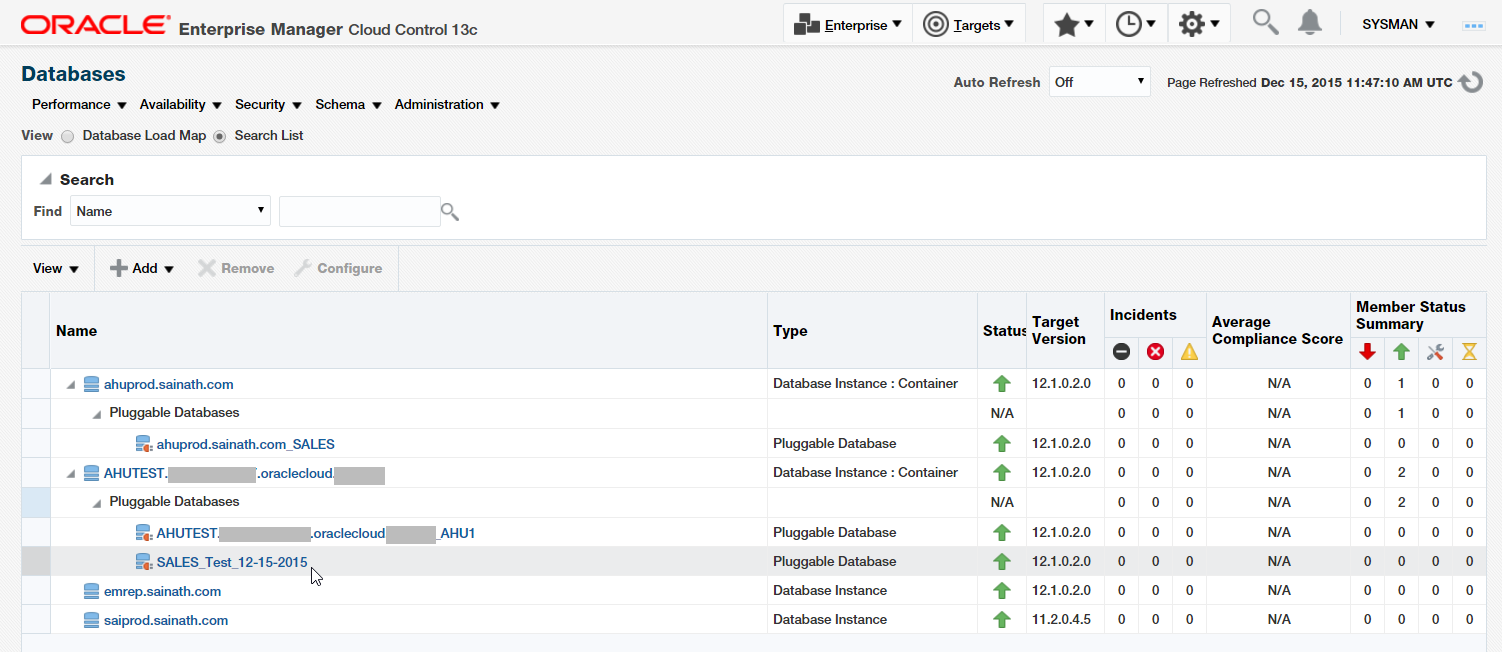
Figure 34: Cloned PDB appears under Cloud CDB
Drill down to the Sales Test PDB Home page (Figure 35).
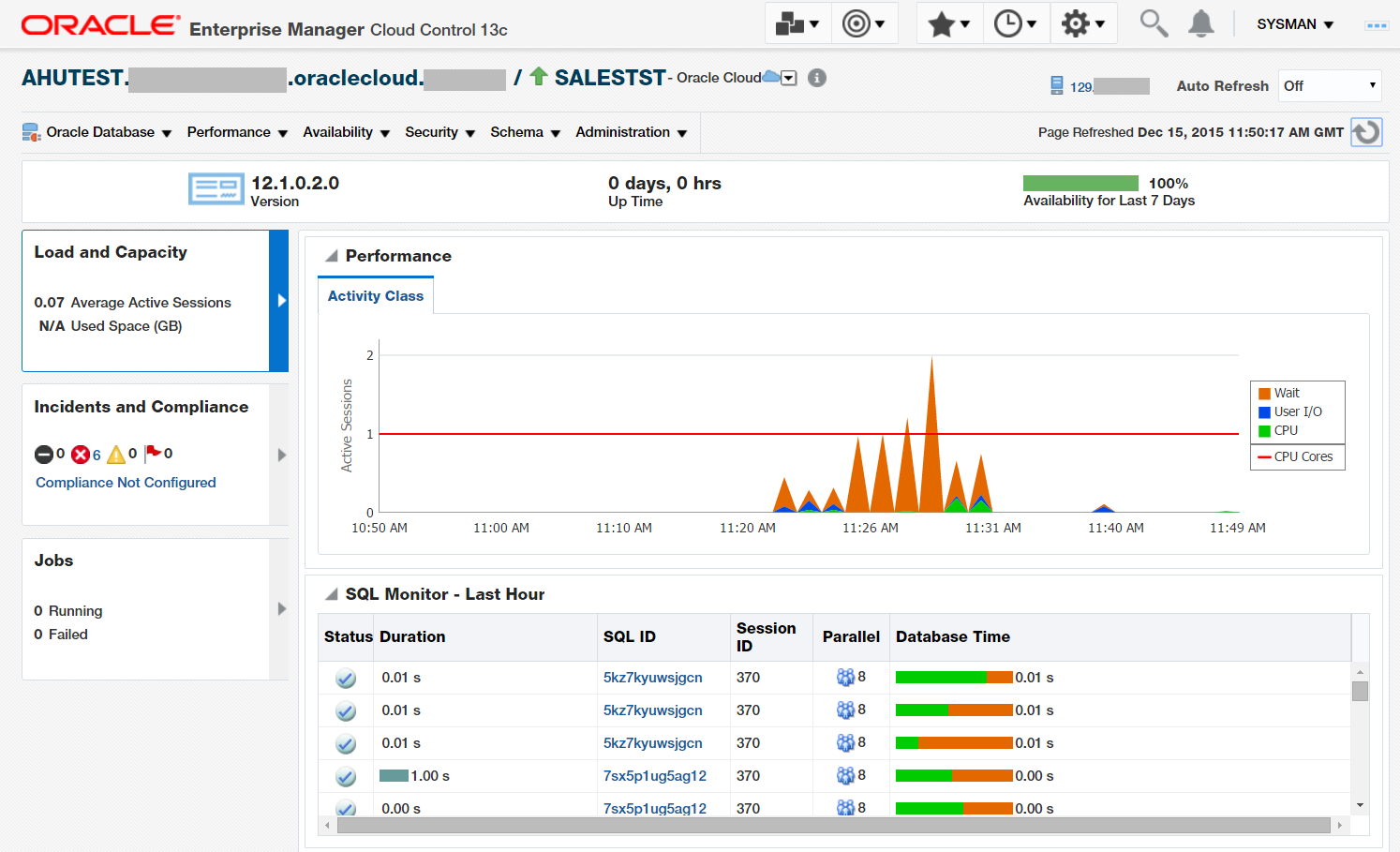
Figure 35: PDB Home Page
Here we can see the newly cloned SALESTST PDB merrily working. We continue examining this PDB in the next part of this article series.
Start the discussion at forums.toadworld.com