Database administration and management is required for any database on which there are continuous business transactions. If databases across enterprises are not monitored and maintained, then such databases are vulnerable to disasters, which eventually brings downtime to missions-critical application and, of course, it will incur losses in the business. Data is now one of the key assets for running a business, globally. Hence, it is one of the major responsibilities of enterprises to invest in resources for database monitoring and management. There are many database management and monitoring tools available for proactive database monitoring. In this article, we will look at PEM – “PostgreSQL Enterprise Manager”.
Postgres Enterprise Manager, or PEM, is a graphical database management/monitoring tool that can help database administrators, system administrators, database developers, database managers, system architects, and performance analysts manage databases efficiently and proactively. PEM has a rich user interface for performing many database administration activities from a single console.
“Why do we need additional software for database management?” Many customers/managers have asked me this and I would like to answer in simple words – “PEM provides a single console for managing and administering single/multiple databases at a single site or across multiple locations . PEM allows full control of databases remotely for better and more efficient database management.
Architecture of Postgres Enterprise Manager:
The diagram below illustrates the Postgres Enterprise Manager Deployment architecture. Postgres Enterprise Manager has three different layers in its deployment.
1 – Postgres Enterprise Manager Server
2 – Postgres Enterprise Manager Agent
3 – Client
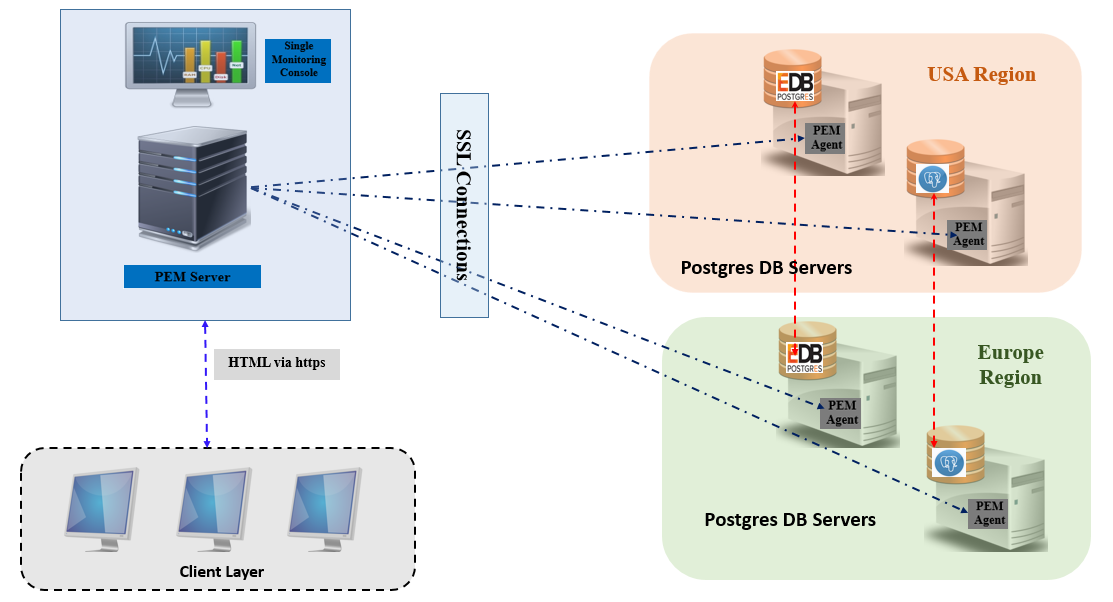
Postgres Enterprise Manager Architecture
Postgres Enterprise Manager Server is the main software, which can be installed on an existing Postgres database server or on a fresh server. PEM Server needs its own database, used for maintaining the EM repository and afor storing information on all its target databases. Currently PEM Server is supported on the Windows and Linux platforms.
Postgres Enterprise Manager Agent is lightweight software that is installed on database server hosts. This software is responsible for connecting to the database and uploading collected statistics to the Postgres Enterprise Manager Server. The information is transported between management agent and management server using SSL certificates.
Client is the end layer, from which all added target databases are monitored. Client has access to the Postgres Enterprise Manager Server secure URL using the “https” protocol and internally Postgres Enterprise Manager Server connects to the database targets as the single management console for one or more local and/or remote databases.
Benefits of Using Postgres Enterprise Manager:
Postgres Enterprise Manager has many benefits, including the following:
1- Robust Management Design: Postgres Enterprise Manager has a robust design for enterprise database administration and management. It was developed for managing multiple local or distributed small/medium/large-scale databases from a single console.
2- Multi-Platform Support: Postgres Enterprise Manager can collect information from PostgreSQL databases running on different OS platforms using remote connection with the Postgres Enterprise Manager Server. It can collect information on overall database activity and publish it on the PEM Server dashboard.
3- GUI-based Administration: Postgres Enterprise Manager supports complete GUI-based administration for all databases that are managed by the PEM Server. You can perform administration activities such as server startup/shutdown, configuration of database parameters, creation of objects, tablespace/datafiles storage management, database backup and recovery and much more.
4- Database Performance Monitoring: PEM provides excellent performance monitoring and performance tuning capabilities for all Postgres databases managed by the PEM Server. It cangather performance statistics from multiple databases and display them on its single dashboard, enabling efficient performance management.
5- Database Alerts: Postgres Enterprise Manager can alerts for configured thresholds. It can send alerts for configured items such as Memory, Disks, CPU etc. Each of these items has a default threshold set, but we can change the threshold values to meet SLAs. Any item exceeding the threshold value will cause an alert on the dashboard and from there an administrator can take corrective action.
6- Capacity Planning: PEM Server keeps its collected database performance metrics for a specified period. The capacity manager utility can help us select a specific time (such as peak load/overloaded/crash) and run an analysis on it, and based on the results it will guide us in corrective capacity planning for resources such as disks, CPU, and memory.
7- Audit Manager: The audit manager works only on Postgres Plus Advanced Server database instances. PEM audit manager can monitor database connections/disconnections from a database server. It can also log SQL statements executed on a database.
8- Postgres Replication: Postgres Enterprise Manager supports streaming replication. The streaming replication wizard is user friendly, enabling you to add new database servers for streaming replication or use an existing replication setup.
9- Log Manager: Can collect server logs with optional requirements and record them in a centralized table. We can use this wizard to customize the log rotation, log destination etc. PEM has separate a tab for the server log dashboard.
10- Expert Database Analysis: Postgres Enterprise Manager has an optional Expert utility that can analyze a database and score it for security best practices, database configuration and other keys areas and generate a report against best practices. We can use the report to configure our database to meet industry best practices.
Those are the top 10 features offered by Postgres Enterprise Manager in my opinion; there are many more features and option available in PEM Server. In the future, I am going to start a series of blog posts that will cover how we can utilize these features for effective and proactive database management of Postgres databases.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learnt about Enterprise DB’s Postgres Enterprise Manager and how can help enterprises achieve proactive database administration and management. PEM offers a competitive set of features for performing almost all database administration activities; its graphical user interface is user friendly. PEM also recommends suggestions and solutions for any reported errors in PEM dashboard. In a forthcoming series of blog posts I will offer how-to articles on Postgres Enterprise Manager.
Start the discussion at forums.toadworld.com