In this article series, we are exploring why and how enterprises are starting to use the PostgreSQL database. In particular we are looking at an enterprise-ready version of PostgreSQL, namely EnterpriseDB Postgres Advanced Server (EDBPAS). This customized version of Postgres is even more closely compatible to the industry leader Oracle, and makes it easier for large enterprises to start using this low-cost database, either on premises or on the cloud. As an example, some large banks have started using EDBPAS for non-core banking applications since they may see it as a good investment for the future.
In the previous parts, we discussed a few basic facts about open-source PostgreSQL – a database more than 20 years old and owned by the Postgres foundation. The EDB version of EDBPAS offers deeper database compatibility for Oracle, with extensive support for PL/SQL, functions and packages, Oracle syntax and semantics, popular Oracle database utilities and interfaces, and bi-directional database replication services.
Two DBMS options are available from the EDB Postgres Platform, namely EDB Postgres Standard, and EDB Postgres Advanced Server (EDBPAS). The latter DBMS option adds additional developer and DBA features, performance, security and database compatibility for Oracle, 24X7 support from EnterpriseDB as well as the EDB-developed tool suites. In addition to the two DBMS options, EDB also offers a deployment of PostGIS, which is an open source extension providing spatial objects and functions. PostGIS when deployed in EDB Postgres inherits the native features of the database deployment, such as scalability and ACID compliance.
We discussed the EDB tool suites that are provided – such as the Integration tool suite, including the EDB Postgres Replication Server that provides single and multi-master replication solutions, the EDB Postgres Data Adapters (foreign data wrappers) used to connect to different database systems, and the EDB Postgres XA (standing for "eXtended Architecture") connector to participate in XA two-phase commit transactions as a local resource manager, working with global transaction managers like Tuxedo.
The second EDB tool suite provided is the Migration tool suite, which consists of the EDB Postgres Migration Toolkit for database migrations from different source databases like Oracle, SQL Server, Sybase and MySQL to PostgreSQL and EDBPAS target databases. The EDB Services team can optionally be engaged for conducting an EDB Postgres Migration Assessment for complex databases with a lot of code. There is also a separate product from Quest, called "SharePlex® for EDB Postgres". This is used to replicate production data from Oracle databases to EDB Postgres databases with zero performance impact, and almost no downtime.
The third EDB tool suite is the Management tool suite with tools for management, monitoring, tuning, high availability, backup and disaster recovery. This includes the EDB Postgres Enterprise Manager which can manage, monitor and tune enterprise-wide Postgres installations from a single console. You can tune your SQL performance with its SQL profiler, monitor and plan your resource requirements through its capacity manager, receive alerts and so on. The Management tool suite also includes the EDB Postgres Failover Manager, which can be used to create a fault-tolerant database cluster, and the EDB Postgres Backup and Recovery tool with simple commands and a system wide catalogue.
Next, we started to discuss the Deployment Options for the EDB Postgres Platform. These range from traditional bare metal up to the latest hybrid cloud configuration. EDB Postgres is quite versatile about where it can be deployed.
First of all, traditional Bare Metal, Virtualization, or Containers can be used to deploy EDB Postgres. Bare Metal means installing on the physical server without any virtualization layers. Of course, multiple virtualization platforms such as VMware, KVM, OpenShift and other Docker-based container platforms are also supported. EDB is also developing a set of containers that intelligently groups various components for ease of use.
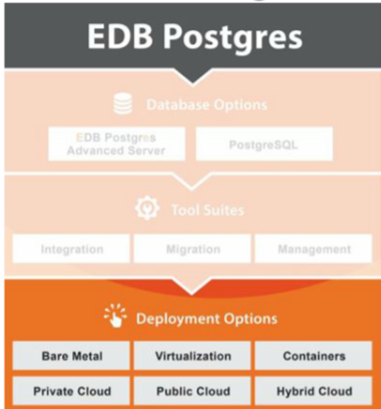
When it comes to the cloud, you can deploy EDB Postgres on the Private cloud, Pubic cloud, or the Hybrid cloud. The Private on-premises cloud is often the first choice for many companies, since it offers full control of your cloud compute and storage with self-service provisioning, and the ability to scale out and scale up. A number of companies are also looking at using the public cloud for their EDB Postgres databases, and you can do so on Amazon AWS, and in the future on Google Cloud and other clouds. This allows you to be flexible with your database deployment and conveniently deploy in any region in the world without setting up your own data center.
And finally, you can also set up a hybrid Postgres database deployment, with applications that span cloud types along with data exchange and replication. We will talk more on EDB Arc – Database as a Service – later on.
On the support side, EnterpriseDB offers 24 X 7 Global production support; such a level of support is considerably important for large enterprises. 10 X 5 Developer support is also available. The professional services on offer have a broad range – they include helping you get started, deployment, migration, Enterprise Architecture services, and also remote DBA services and technical account management. The support and engineering teams are co-located so as to maximize their efficiency. In the Remote DBA service, certified DBAs are provided by EDB; and these can be utilized by enterprises in EDB Postgres deployments, which would obviously work out to be cost effective as compared to a full time DBA.
The certifications offered by EnterpriseDB are said to be an industry-recognized global standard. There are PostgreSQL and EDB Postgres programs – Associate level and Professional level with a convenient online exam format. Training offered is either classroom based, or on-site, or online eSubscriptions with DBA or Developer tracks. The courses cover administration, migration, performance tuning and other advanced topics.
For the licensing of the software itself, there are three different subscription models available for EDB Postgres – these include Enterprise, Standard and Developer subscriptions. All subscription models include databases, management suites, integration suites and the migration suites. You can choose a subscription model that matches your needs, depending on the database you want to use.
The Standard subscription does not include EDB Postgres Advanced Server, only PostgreSQL. The Enterprise subscription includes the former and not the latter. The Developer subscription includes both. The other difference is that the Standard subscription does not include the XA connector used for Distributed Transaction management; this is included in the other two subscriptions.
We continue in the next part of this article series.
Start the discussion at forums.toadworld.com