MySQL database is the leading open source database. Toad Edge is a database development and administration integrated development environment (IDE) for MySQL database with support to be added for some of the other open source databases. In an earlier article Using Toad Edge with MySQL Database we introduced using Toad Edge with MySQL Database. We have also discussed using Toad Edge to access and manage MySQL database with various cloud managed services for MySQL – AWS RDS Aurora DB, IBM Bluemix, and Oracle Cloud Platform. In two articles we shall discuss the following Toad Edge features, some of which have not been discussed earlier:
- Access and manage MySQL Database on Docker
- Create a new database with the New Database wizard
- Create a new database table with the New Table wizard
- Text Search (added in Toad Edge 1.1)
- Import Data with the Import Data wizard
- The “Active Database” is called the “Default Database” in Toad Edge 1.1
In the first of the two articles we shall discuss running MySQL database on Docker engine and connecting to the database with Toad Edge 1.1. The other features listed shall be discussed in a subsequent article.
Why use MySQL Database with Docker
If not using a managed service the following procedure is typical to be able to use MySQL database.
- Download the MySQL Database Binaries on an OS
- Install MySQL Database
- Configure MySQL database, including port configuration, setting password for root user, and creating a service.
The preceding is for using MySQL database on just a single node. And if MySQL is to be used on multiple nodes, MySQL Cluster Database has to be used.
Docker containers have introduced a lightweight alternative to running software and applications. A Docker container is created with a Docker image, which is based on a Dockerfile. A Dockerfile specifies all the instructions for downloading the required software and dependencies, extracting the binaries, installing software, setting environment variables, starting the required applications, and optionally exposing port/s on the container at which the application running in a container may be accessed. A Docker container is similar to a virtual machine in that it runs on a host OS, but a Docker container is more different than similar to a virtual machine. While a virtual machine makes use of a whole OS, a Docker container only makes use of a snapshot of the underlying OS. Multiple Docker containers may run in isolation on a single OS with each container having its own networking and filesystem. To run an application on multiple nodes the Docker Swarm mode was introduced in Docker v 1.12. Docker Swarm mode creates a Swarm consisting of one or more nodes and a Docker service deployed on the Swarm runs tasks (Docker containers) on one or more of these nodes. A Docker service may optionally expose port/s on the host machines for ingress access by a client application. A client application for this tutorial would be Toad Edge.
In this tutorial we shall discuss running MySQL database on a cluster of three EC2 instances by using a Docker service on Docker Swarm mode. This tutorial has the following sections.
- Setting the Environment
- Creating a Docker Swarm
- Creating a Docker Service for MySQL
- Connecting to MySQL Database in Toad Edge
Setting the Environment
Docker is preinstalled on Container Linux by CoreOS. Select the Container Linux by CoreOS AMI to start three EC2 instances as shown in Figure 1.
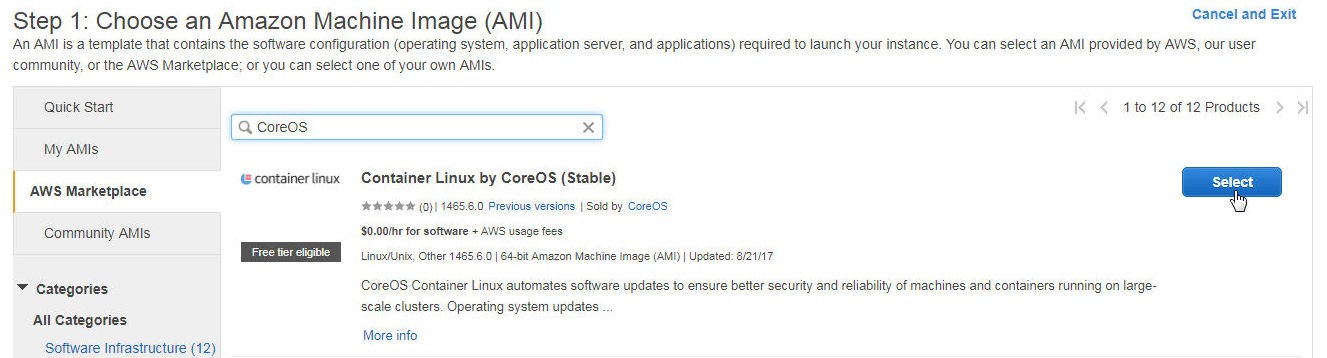
Figure 1. Selecting AMI for EC2 Instances
Specify Number of Instances as 3 as shown in Figure 2.
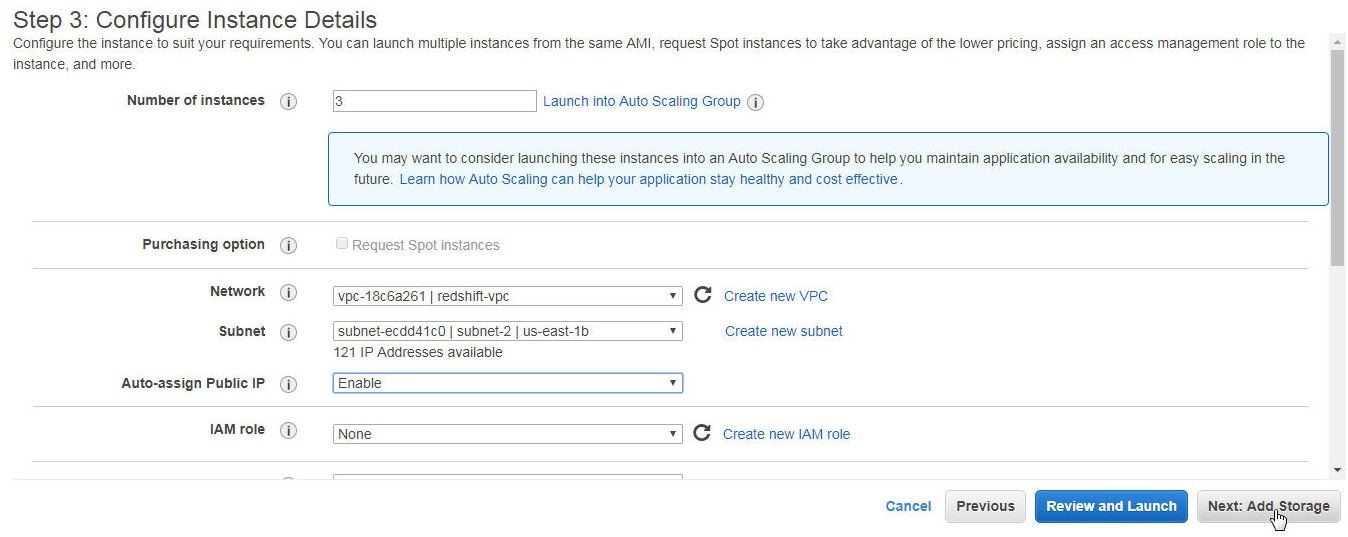
Figure 2. Specifying Number of Instances as 3
Three EC2 instances based on the CoreOS AMI get launched, as shown in Figure 3. We shall subsequently create a Docker Swarm on the EC2 instances.
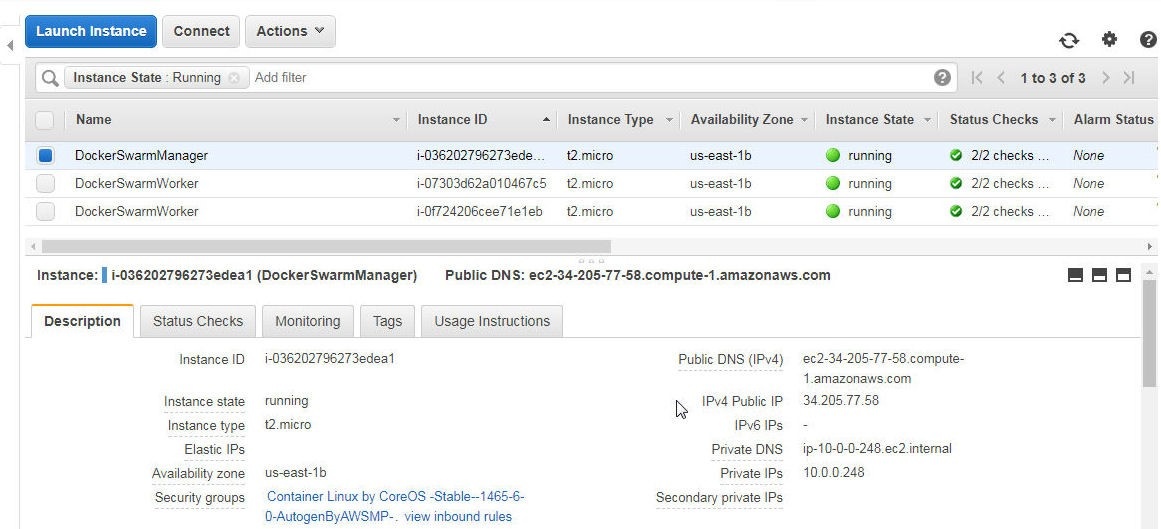
Figure 3. EC2 Instances for Docker Swarm
Creating a Docker Swarm
A Docker Swarm consists of at least one manager node and zero or more worker nodes. First, we need to initialize the Swarm mode. SSH Login into the EC2 instance for Swarm manager using the Public IP Address of the instance from the EC2 management console as shown in Figure 3.
ssh -i "coreos.pem" core@34.205.77.58
Using the Private IP of the manager instance initialize the Swarm with the following command.
docker swarm init --advertise-addr 10.0.0.248
Swarm gets initialized and the current node becomes the manager node as shown in the output to the command in Figure 4. A docker swarm join command is also output that we shall use to join worker nodes with the Swarm.
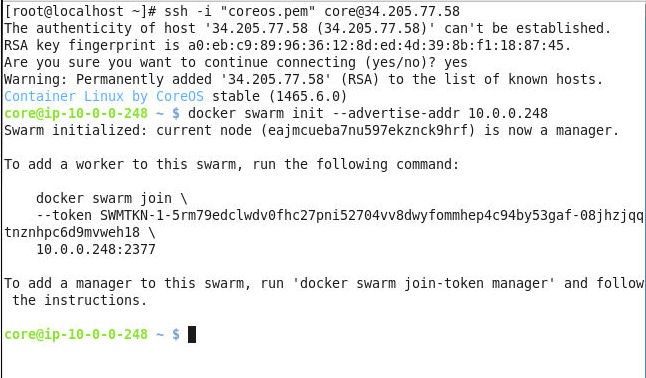
Figure 4. Initializing the Docker Swarm
List the Docker nodes.
docker node ls
The manager node is the only node in the Swarm to start with, as shown in Figure 5.
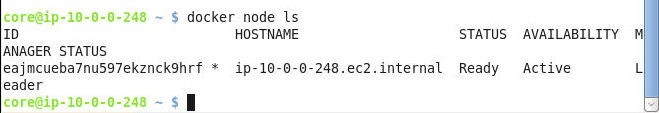
Figure 5. Listing Swarm Nodes
Next, join two worker nodes to the Swarm. SSH Login into an EC2 instance started for a worker node.
ssh -i "coreos.pem" core@510.0.0.248
Run the docker swarm join command output when the Swarm is initialized. The worker node joins the Swarm, as shown in Figure 6.
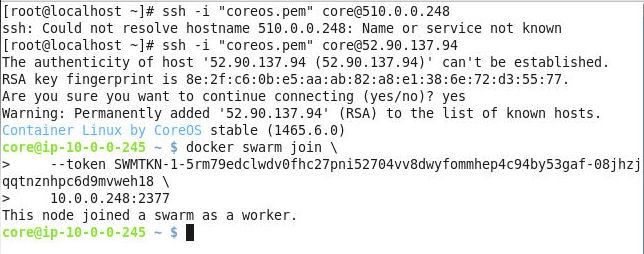
Figure 6. Joining a Worker Node to the Swarm
Similarly, SSH login into the other worker instance.
ssh -i "coreos.pem" core@52.90.45.217
Run the same docker swarm join command to join the other worker node to the Swarm as shown in Figure 7.
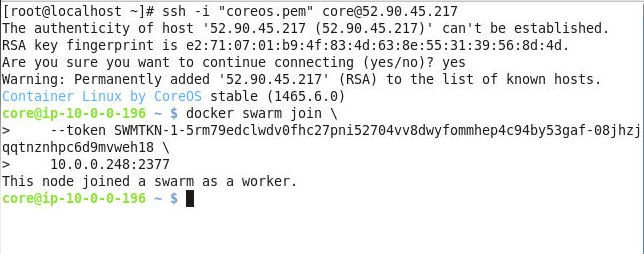
Figure 7. Joining the 2nd Worker Node to the Swarm
List the Swarm nodes.
docker node ls
The three nodes in the Swarm get listed, as shown in Figure 8.
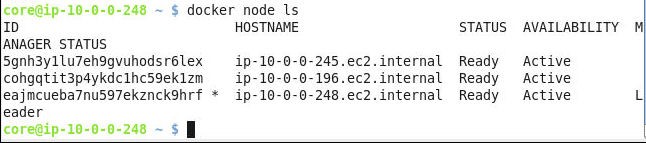
Figure 8. Listing Swarm Nodes
Creating a Docker Service for MySQL
In this section we shall create a Docker service for MySQL database. The docker service create command is used to create a Docker service and the Docker image used for the service is a command parameter. The mysql Docker image has a mandatory environment variable MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD that must be specified in the command. The number of replicas to be set is specified with the –replicas option. The service name is specified with the –name option. Docker service must be exposed on the host port so that Toad Edge may connect with the service. A Docker service exposes a port on the host/s with the –p or –publish option. Run the following command on Swarm manager (not a Swarm worker node).
docker service create
--replicas 3
-p 3306:3306
--env MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD='mysql'
--name mysql
mysql
A Docker service gets created. List the Docker services.
docker service ls
The mysql service gets listed. List the Service tasks.
docker service ps mysql
The three tasks in the service get listed. The output from the preceding commands is shown in Figure 9.
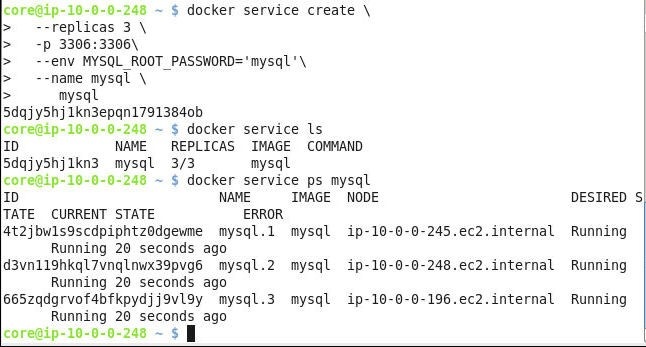
Figure 9. Creating a Docker Service and Listing Service Tasks
Connecting to MySQL Database in Toad Edge
In this section we shall connect with MySQL database running on a Docker Swarm with Toad Edge. Select Connect>New Connection in Toad Edge as shown in Figure 10.
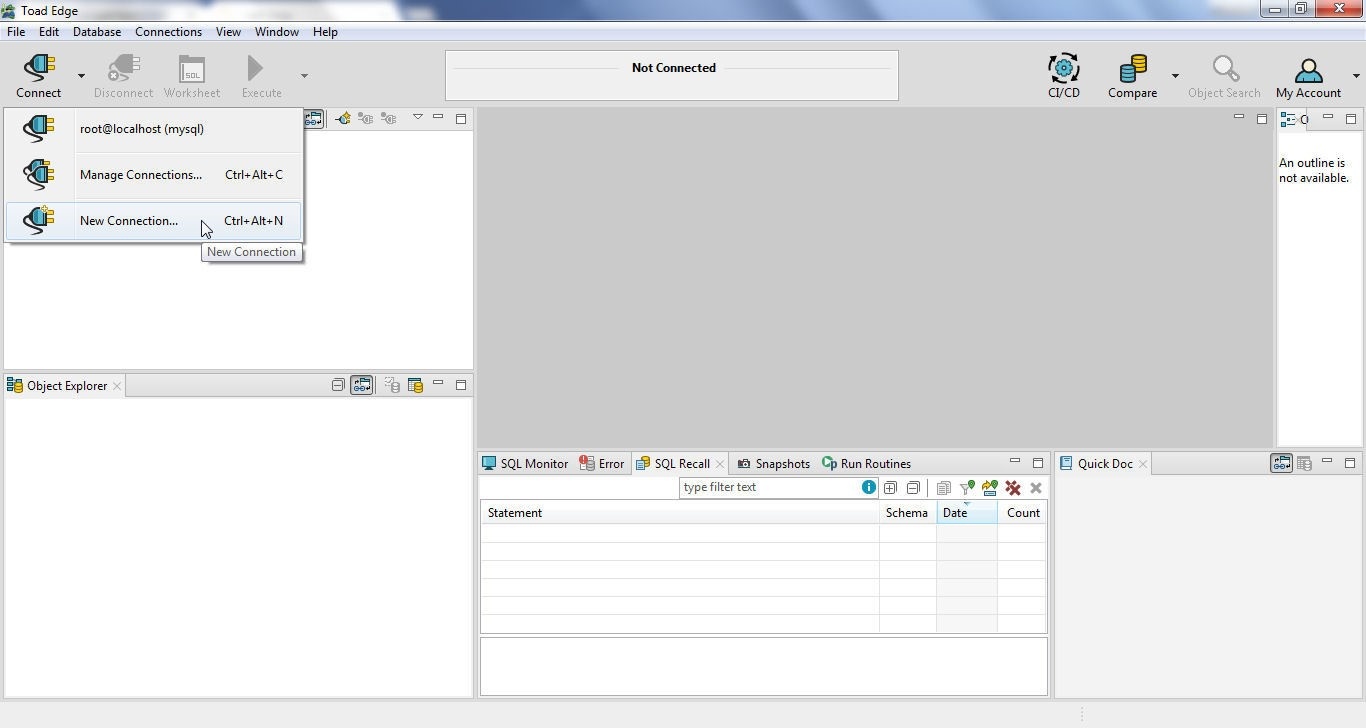
Figure 10. Connect>New Connection
The New MySQL Connection wizard gets launched. To be able to connect to MySQL on Docker we need to specify a Host in the New MySQL Connection wizard. The Host is the Public DNS of one (any) of the EC2 instances on which the Docker Swarm is running. Obtain the Public DNS of the Swarm manager node as shown in Figure 11.
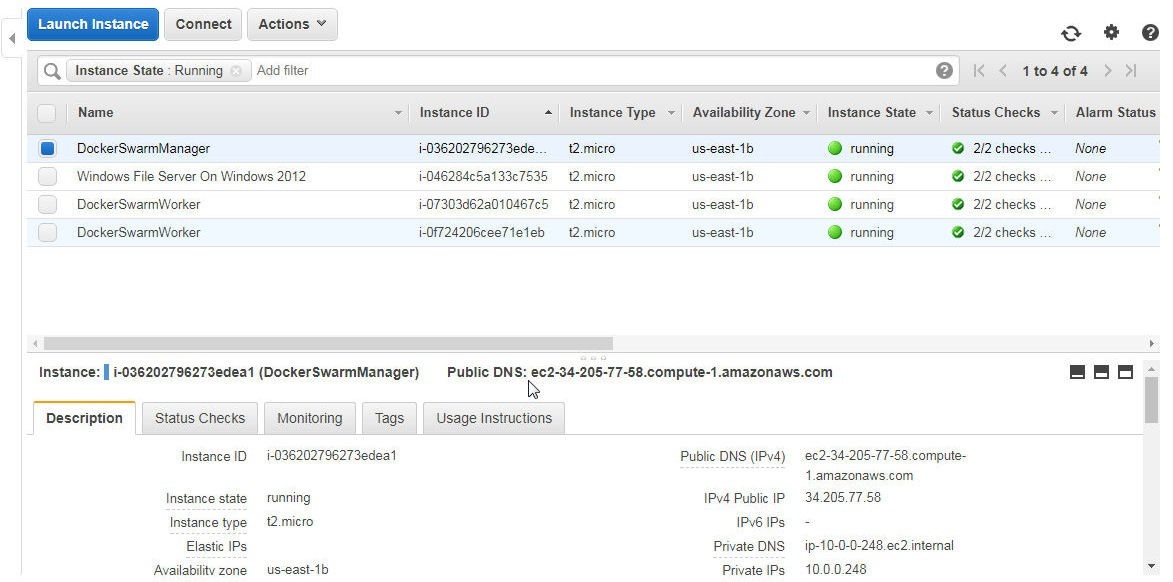
Figure 11. Pubic DNS of the Swarm Manager
Specify the Public DNS in the Host field as shown in Figure 12. Specify Database as mysql and Port as 3306. Specify User as root and Password as the password set when creating the Docker service. Keep the option Enable AutoCommit selected. Click on Test Connection to test the connection as shown in Figure 12.
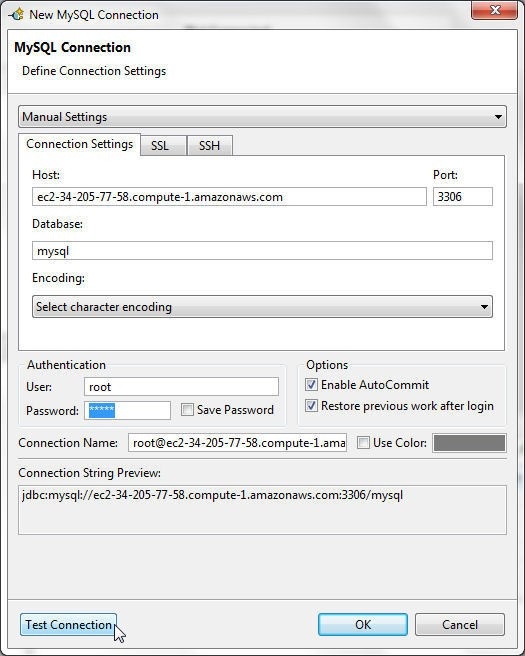
Figure 12. Testing Connection
If a connection gets established the output is Connection is OK, as shown in Figure 13. Click on OK.
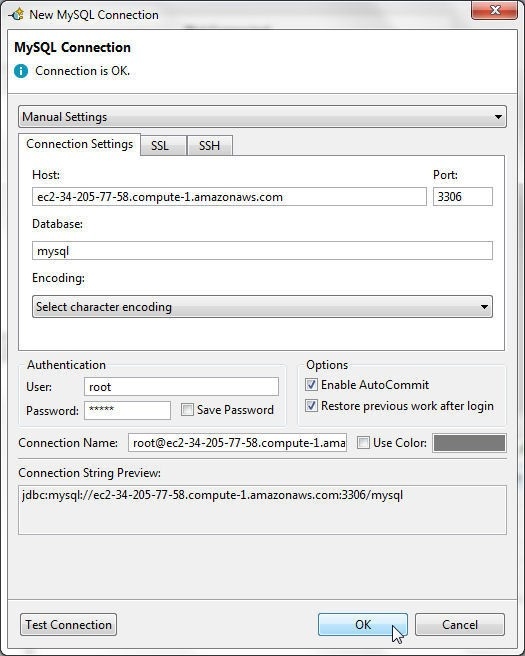
Figure 13. Completing MySQL Connection Configuration
A new connection gets added to the Connections view as shown in Figure 14.
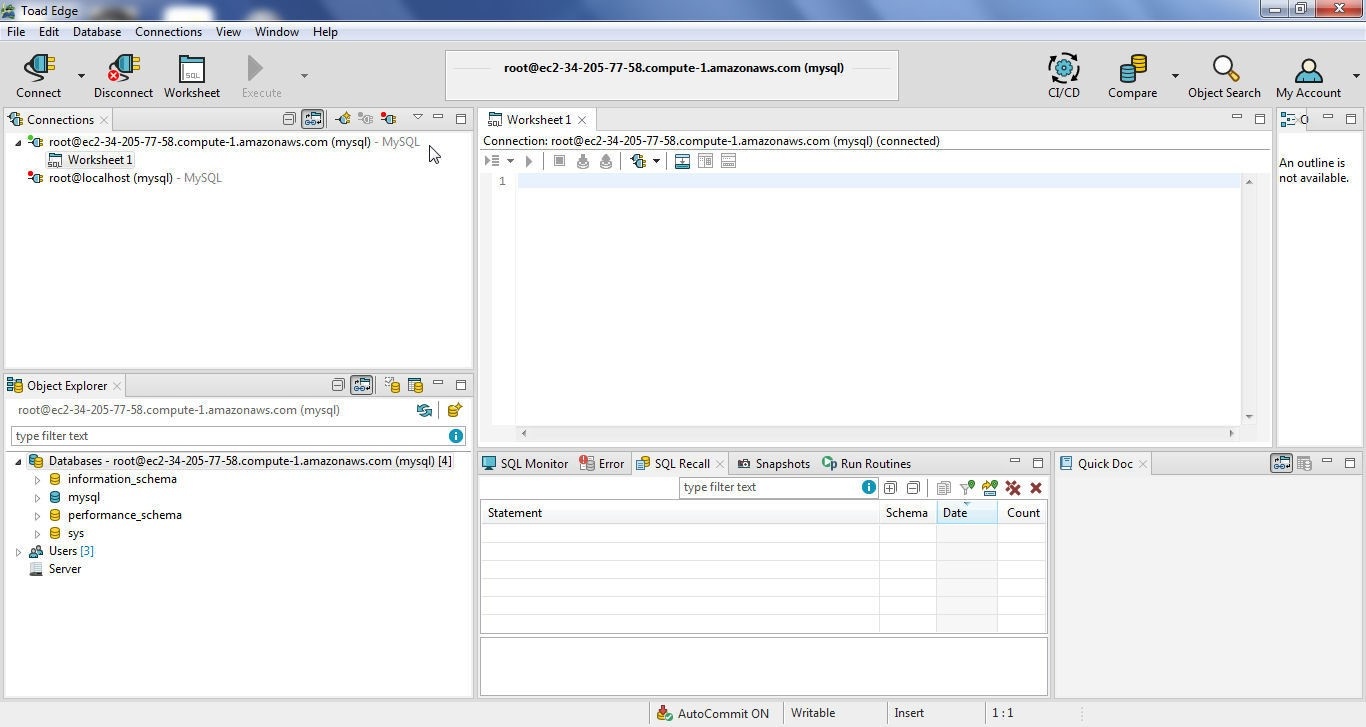
Figure 14. New Connection Added
A new connection is associated with a SQL Worksheet which gets created when a new connection is created. The Object Explorer lists the databases. The active or the default database is blue (ish) color and is mysql, as shown in Figure 15.
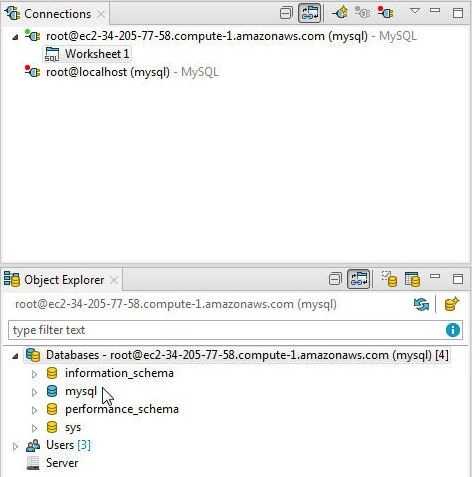
Figure 15. Object Explorer>Databases
A MySQL database driver is configured by default in Toad Edge. To find the driver configured select View>Preferences>Database as shown in Figure 16.
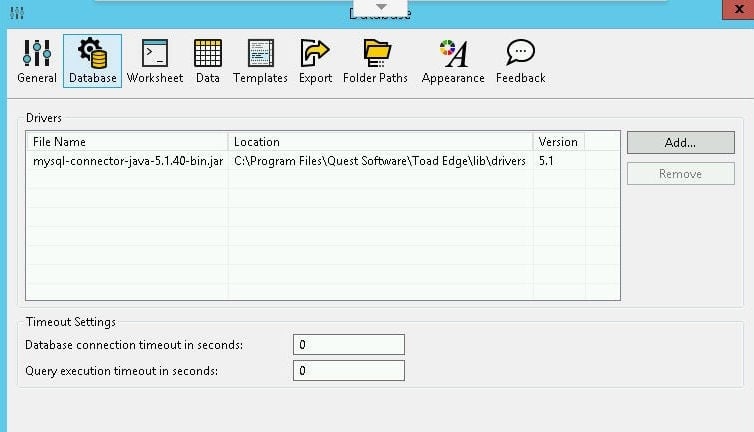
Figure 16. View>Preferences>Database
Conclusion
In this article we discussed using Toad Edge 1.1 with MySQL Database on Docker. The benefits of Docker include a lightweight container based OS environment, convenience of running MySQL database with a single command, and making the MySQL database service available on multiple nodes in a Docker Swarm. In a continuation article we shall discuss some of the other Toad Edge features some of which are introduced in Toad Edge 1.1.
Start the discussion at forums.toadworld.com